Pulmonary sequelae in a patient recovered from swine flu
- PMID: 22919170
- PMCID: PMC3424870
- DOI: 10.4103/0970-2113.99118
Pulmonary sequelae in a patient recovered from swine flu
Abstract
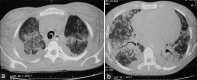
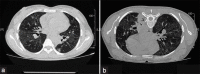
The pandemic of swine flu (H1N1) influenza spread to involve the whole world rapidly. Many patients manifested a mild clinical illness but some developed pneumonia and respiratory failure. High mortality was observed in patients with severe disease. Among survivors, studies are limited. Ground-glass opacities on a high-resolution computerized tomography scan and reduced diffusion capacity were noted after 3 months in a study. But long-term complications in patients with swine flu pneumonia have not been studied well. We are presenting an unusual case of swine flu pneumonia who developed interstitial lung disease after recovery.
Keywords: Complications; Influenza A virus H1N1 subtype; diffuse parenchymal lung disease; pulmonary fibrosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Chest Radiological Findings of Patients With Severe H1N1 Pneumonia Requiring Intensive Care.J Intensive Care Med. 2016 Jan;31(1):51-60. doi: 10.1177/0885066614538753. Epub 2014 Jun 12. J Intensive Care Med. 2016. PMID: 24923491
-
[Influence of concomitant illness on clinical manifestations and severity of A/H1N1 influenza infection among patients hospitalized in the Hospital of Infectious Diseases in Warsaw--clinical cases].Przegl Epidemiol. 2010;64(1):21-5. Przegl Epidemiol. 2010. PMID: 20499655 Polish.
-
[Comparison between pandemic H1N1 2009 influenza pneumonia and seasonal influenza pneumonia in adults].Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 2011 Apr;49(4):255-65. Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 2011. PMID: 21591453 Japanese.
-
Non respiratory manifestations of swine flu.Clin Ter. 2009;160(6):499-501. Clin Ter. 2009. PMID: 20198294 Review.
-
Influenza A(H1N1)pdm09-related pneumonia and other complications.Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2012 Oct;30 Suppl 4:43-8. doi: 10.1016/S0213-005X(12)70104-0. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2012. PMID: 23116792 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Flu and pulmonary fibrosis.Lung India. 2013 Apr;30(2):95-6. doi: 10.4103/0970-2113.110412. Lung India. 2013. PMID: 23741087 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Macrophage PPAR-γ suppresses long-term lung fibrotic sequelae following acute influenza infection.PLoS One. 2019 Oct 4;14(10):e0223430. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0223430. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31584978 Free PMC article.
-
Organizing pneumonia in swine flu.Lung India. 2013 Oct;30(4):376-7. doi: 10.4103/0970-2113.120625. Lung India. 2013. PMID: 24339511 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Authors' reply.Lung India. 2013 Oct;30(4):377-8. Lung India. 2013. PMID: 24339512 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Organizing pneumonia as a pulmonary sequela of swine flu.Lung India. 2013 Apr;30(2):171. doi: 10.4103/0970-2113.110440. Lung India. 2013. PMID: 23741106 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Perez-Padilla R, de la Rosa-Zamboni D, Ponce de Leon S, Hernandez M, Quiñones-Falconi F, Bautista E, et al. Pneumonia and respiratory failure from swine-origin influenza A (H1N1) in Mexico. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:680–9. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). Pandemic (H1N1) 2009. Update 91. [Last accessed on 2010 Mar 12]. Available from: http://www.who.int/csr/don/2010_03_12/en/index.html .
-
- Jaime MB, Luis AG, Luis MD, Ixchel CM, Patricio SD. Parenchymal injury, fibrosis, and pneumatocele in an H1N1-positive patient. Chest. 2010;138:38A.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

