Time course of inflammatory cytokines in acute ischemic stroke patients and their relation to inter-alfa trypsin inhibitor heavy chain 4 and outcome
- PMID: 22919189
- PMCID: PMC3424794
- DOI: 10.4103/0972-2327.99707
Time course of inflammatory cytokines in acute ischemic stroke patients and their relation to inter-alfa trypsin inhibitor heavy chain 4 and outcome
Abstract
Background: Biomarker for prognosis of stroke is urgently needed for the management of acute ischemic stroke (AIS) patients.
Objective: To evaluate the course of inflammatory cytokines in AIS patients and its comparison with inter-alfa trypsin inhibitor heavy chain 4 (ITIH4) and outcome after AIS.
Materials and methods: A panel of 12 inflammatory cytokines and ITIH4 were estimated in serial blood samples collected at admission, 24 h, 48 h, 72 h, 144 h and at discharge of AIS patients (n = 5).
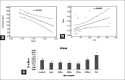
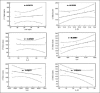
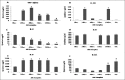
Results: Out of the 12 cytokines, only interleukin (IL)-2, tumor necrosis factor-alfa (TNF-α), IL-10, IL-6, IL-1B and IL-8 were in the measurable range of the kit (10 pg/mL). We found high IL-2 at admission, which decreased (P < 0.05) in the follow-up samples. TNF-α initially increases (P < 0.05) at 24 h followed by gradual decrease (P < 0.05) after 72 h. IL-10 decreases initially (P < 0.05) till 72 h as compared with its level at admission and then increases (P < 0.05) after 144 h. Similarly, ITIH4 was down-regulated in the early 72 h followed by further increase with improvement of the patient. ITIH4 correlates with IL-10 and computed tomography scan infarct volume. Serum IL-6, IL-1B and IL-8 increased in the AIS patients, but did not show any pattern.
Conclusions: Serial measurement of IL-10, IL-2 and TNF-α and ITIH4 may be useful for the follow-up of clinical outcome after AIS.
Keywords: Acute ischemic stroke; cytokine; inter-alfa trypsin inhibitor heavy chain 4; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Barone FC, Feuerstein GZ. Inflammatory mediators and stroke: New opportunities for novel therapeutics. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1999;19:819–34. - PubMed
-
- Samson Y, Lapergue B, Hosseini H. [Inflammation and ischaemic stroke: Current status and future perspectives] Rev Neurol (Paris) 2005;161:1177–82. - PubMed
-
- Zhang RL, Chopp M, Li Y, Zaloga C, Jiang N, Jones ML, et al. Anti-ICAM-1 antibody reduces ischemic cell damage after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat. Neurology. 1994;44:1747–51. - PubMed
-
- Matsuo Y, Onodera H, Shiga Y, Shozuhara H, Ninomiya M, Kihara T, et al. Role of cell adhesion molecules in brain injury after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat. Brain Res. 1994;656:344–52. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

