Inflammation- and stress-related signaling pathways in hepatocarcinogenesis
- PMID: 22919237
- PMCID: PMC3422785
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i31.4071
Inflammation- and stress-related signaling pathways in hepatocarcinogenesis
Abstract
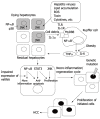
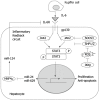
It has been established that cancer can be promoted and exacerbated by inflammation. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the fifth most common cancer worldwide, and its long-term prognosis remains poor. Although HCC is a complex and heterogeneous tumor with several genomic mutations, it usually develops in the context of chronic liver damage and inflammation, suggesting that understanding the mechanism(s) of inflammation-mediated hepatocarcinogenesis is essential for the treatment and prevention of HCC. Chronic liver damage induces a persistent cycle of necro-inflammation and hepatocyte regeneration, resulting in genetic mutations in hepatocytes and expansion of initiated cells, eventually leading to HCC development. Recently, several inflammation- and stress-related signaling pathways have been identified as key players in these processes, which include the nuclear factor-κB, signal transducer and activator of transcription, and stress-activated mitogen- activated protein kinase pathways. Although these pathways may suggest potential therapeutic targets, they have a wide range of functions and complex crosstalk occurs among them. This review focuses on recent advances in our understanding of the roles of these signaling pathways in hepatocarcinogenesis.
Keywords: Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Inflammation; Mitogen-activated protein kinase; Nuclear factor-κB; Signal transducer and activator of transcription; Transforming growth factor-activated kinase 1; c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase; p38.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 inhibits hepatocarcinogenesis by controlling the tumor-suppressing function of stress-activated mitogen-activated protein kinase.Hepatology. 2011 Jul;54(1):185-95. doi: 10.1002/hep.24357. Hepatology. 2011. PMID: 21488081
-
Canonical NF-κB signaling in hepatocytes acts as a tumor-suppressor in hepatitis B virus surface antigen-driven hepatocellular carcinoma by controlling the unfolded protein response.Hepatology. 2016 May;63(5):1592-607. doi: 10.1002/hep.28435. Epub 2016 Mar 4. Hepatology. 2016. PMID: 26892811
-
Growth-hormone-induced signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 signaling causes gigantism, inflammation, and premature death but protects mice from aggressive liver cancer.Hepatology. 2012 Mar;55(3):941-52. doi: 10.1002/hep.24765. Epub 2012 Jan 13. Hepatology. 2012. PMID: 22031092
-
Pleiotropic effects of methionine adenosyltransferases deregulation as determinants of liver cancer progression and prognosis.J Hepatol. 2013 Oct;59(4):830-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.04.031. Epub 2013 May 7. J Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23665184 Review.
-
Targeting molecular signal transduction pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma and its implications for cancer therapy.Cell Biol Int. 2021 Nov;45(11):2161-2177. doi: 10.1002/cbin.11670. Epub 2021 Aug 1. Cell Biol Int. 2021. PMID: 34270844 Review.
Cited by
-
Increased Expression of Programmed Death-Ligand 1 in Infiltrating Immune Cells in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Tissues after Sorafenib Treatment.Liver Cancer. 2019 Mar;8(2):110-120. doi: 10.1159/000489021. Epub 2018 Jun 15. Liver Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31019901 Free PMC article.
-
Cell fate analysis of zone 3 hepatocytes in liver injury and tumorigenesis.JHEP Rep. 2021 May 27;3(4):100315. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2021.100315. eCollection 2021 Aug. JHEP Rep. 2021. PMID: 34345813 Free PMC article.
-
Potential role of pentraxin 3 (PTX3) and aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) in liver cirrhotic patients: predicting and diagnostic impact in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) development.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Aug 13;52(1):826. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10909-1. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40802153
-
Plasma membrane gp96 enhances invasion and metastatic potential of liver cancer via regulation of uPAR.Mol Oncol. 2015 Aug;9(7):1312-23. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2015.03.004. Epub 2015 Mar 24. Mol Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25841765 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Activation, Exhaustion and Senescence Profiles as Possible Predictors of Cancer in Liver Transplanted Patients.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 13;12:899170. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.899170. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35769714 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balkwill F, Mantovani A. Inflammation and cancer: back to Virchow? Lancet. 2001;357:539–545. - PubMed
-
- El-Serag HB. Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:1118–1127. - PubMed
-
- Masuzaki R, Yoshida H, Tateishi R, Shiina S, Omata M. Hepatocellular carcinoma in viral hepatitis: improving standard therapy. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2008;22:1137–1151. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

