Oxymatrine liposome attenuates hepatic fibrosis via targeting hepatic stellate cells
- PMID: 22919254
- PMCID: PMC3422802
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i31.4199
Oxymatrine liposome attenuates hepatic fibrosis via targeting hepatic stellate cells
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the potential mechanism of Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) peptide-labeled liposome loading oxymatrine (OM) therapy in CCl₄-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats.
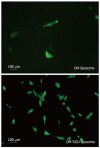
Methods: We constructed a rat model of CCl₄-induced hepatic fibrosis and treated the rats with different formulations of OM. To evaluate the antifibrotic effect of OM, we detected levels of alkaline phosphatase, hepatic histopathology (hematoxylin and eosin stain and Masson staining) and fibrosis-related gene expression of matrix metallopeptidase (MMP)-2, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP)-1 as well as type I procollagen via quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. To detect cell viability and apoptosis of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), we performed 3-(4,5)-dimethylthiahiazo(-z-y1)-3,5-diphenytetrazoliumromide assay and flow cytometry. To reinforce the combination of oxymatrine with HSCs, we constructed fluorescein-isothiocyanate-conjugated Arg-Gly-Asp peptide-labeled liposomes loading OM, and its targeting of HSCs was examined by fluorescent microscopy.
Results: OM attenuated CCl₄-induced hepatic fibrosis, as defined by reducing serum alkaline phosphatase (344.47 ± 27.52 U/L vs 550.69 ± 43.78 U/L, P < 0.05), attenuating liver injury and improving collagen deposits (2.36% ± 0.09% vs 7.70% ± 0.60%, P < 0.05) and downregulating fibrosis-related gene expression, that is, MMP-2, TIMP-1 and type I procollagen (P < 0.05). OM inhibited cell viability and induced apoptosis of HSCs in vitro. RGD promoted OM targeting of HSCs and enhanced the therapeutic effect of OM in terms of serum alkaline phosphatase (272.51 ± 19.55 U/L vs 344.47 ± 27.52 U/L, P < 0.05), liver injury, collagen deposits (0.26% ± 0.09% vs 2.36% ± 0.09%, P < 0.05) and downregulating fibrosis-related gene expression, that is, MMP-2, TIMP-1 and type I procollagen (P < 0.05). Moreover, in vitro assay demonstrated that RGD enhanced the effect of OM on HSC viability and apoptosis.
Conclusion: OM attenuated hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting viability and inducing apoptosis of HSCs. The RGD-labeled formulation enhanced the targeting efficiency for HSCs and the therapeutic effect.
Keywords: Arg-Gly-Asp peptide; Hepatic fibrosis; Hepatic stellate cell; Oxymatrine; Target therapy.
Figures



References
-
- Friedman SL. Molecular regulation of hepatic fibrosis, an integrated cellular response to tissue injury. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:2247–2250. - PubMed
-
- Kastanis GJ, Hernandez-Nazara Z, Nieto N, Rincón-Sanchez AR, Popratiloff A, Dominguez-Rosales JA, Lechuga CG, Rojkind M. The role of dystroglycan in PDGF-BB-dependent migration of activated hepatic stellate cells/myofibroblasts. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011;301:G464–G474. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kim MR, Kim HS, Lee MS, Lee MJ, Jang JJ. Cell cycle protein profile of the hepatic stellate cells(HSCs)in dimethylnitrosamine-induced rat hepatic fibrosis. Exp Mol Med. 2005;37:335–342. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, Liu P, Gao X, Qian W, Xu K. rAAV2-TGF-β(3) decreases collagen synthesis and deposition in the liver of experimental hepatic fibrosis rat. Dig Dis Sci. 2010;55:2821–2830. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

