Biological activity of lenalidomide and its underlying therapeutic effects in multiple myeloma
- PMID: 22919394
- PMCID: PMC3417169
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/842945
Biological activity of lenalidomide and its underlying therapeutic effects in multiple myeloma
Abstract
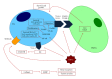
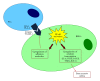
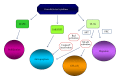
Lenalidomide is a synthetic compound derived by modifying the chemical structure of thalidomide. It belongs to the second generation of immunomodulatory drugs (IMiDs) and possesses pleiotropic properties. Even if lenalidomide has been shown to be active in the treatment of several hematologic malignancies, this review article is mostly focalized on its mode of action in multiple myeloma. The present paper is about the direct and indirect antitumor effects of lenalidomide on malignant plasmacells, bone marrow microenvironment, bone resorption and host's immune response. The molecular mechanisms and targets of lenalidomide remain largely unknown, but recent evidence shows cereblon (CRBN) as a possible mediator of its therapeutical effects.
Figures
References
-
- List A, Kurtin S, Roe DJ, et al. Efficacy of lenalidomide in myelodysplastic syndromes. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2005;352(6):549–557. - PubMed
-
- List AF. Lenalidomide: from bench to bedside (part 1) Cancer Control. 2006;13(supplement 2-3) - PubMed
-
- List AF, Baker AF, Green S, Bellamy W. Lenalidomide: targeted anemia therapy for myelodysplastic syndromes. Cancer Control. 2006;13(supplement 4–11) - PubMed
-
- Raza A, Reeves JA, Feldman EJ, et al. Phase 2 study of lenalidomide in transfusion-dependent, low-risk, and intermediate-1-risk myelodysplastic syndromes with karyotypes other than deletion 5q. Blood. 2008;111(1):86–93. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources