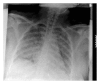
Neurogenic pulmonary edema associated with underlying lung disease after a breakthrough seizure
- PMID: 22919397
- PMCID: PMC3419427
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/560942
Neurogenic pulmonary edema associated with underlying lung disease after a breakthrough seizure
Abstract
Neurogenic pulmonary edema (NPE) can result from various central nervous system disorders such as brain malignancies, traumatic brain injuries, infections, and seizures. Although the pathogenesis is not completely understood, NPE creates an increase in pulmonary interstitial and alveolar fluid. It has been reported with prolonged seizure activity. Treatment for NPE is largely supportive. If unrecognized, it can lead to hypoxia and respiratory arrest. We report a case of NPE in a middle-aged female patient following a breakthrough seizure in whom an immunological cause for respiratory findings was high on the differential list, based on her past medical history and chronicity of symptoms. Rapid symptomatic and radiological improvement following hospitalization led to the correct diagnosis.
Figures
References
-
- Colice GL, Matthay MA, Bass E, Matthay RA. Neurogenic pulmonary edema. American Review of Respiratory Disease. 1984;130(5):941–948. - PubMed
-
- Simon RP. Neurogenic pulmonary edema. Neurologic Clinics. 1993;11(2):309–323. - PubMed
-
- Ohlmacher AP. Acute pulmonary edema as a terminal event in certain forms of epilepsy. The American Journal of the Medical Sciences. 1910;139:417–422.
-
- Leestma JE, Walczak T, Hughes JR, Kalelkar MB, Teas SS. A prospective study on sudden unexpected death in epilepsy. Annals of Neurology. 1989;26(2):195–203. - PubMed
-
- Terrence CF, Rao GR, Perper JA. Neurogenic pulmonary edema in unexpected, unexplained death of epileptic patients. Annals of Neurology. 1981;9(5):458–464. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous