Green Tea Extract Ameliorates Learning and Memory Deficits in Ischemic Rats via Its Active Component Polyphenol Epigallocatechin-3-gallate by Modulation of Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation
- PMID: 22919410
- PMCID: PMC3419441
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/163106
Green Tea Extract Ameliorates Learning and Memory Deficits in Ischemic Rats via Its Active Component Polyphenol Epigallocatechin-3-gallate by Modulation of Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation
Abstract
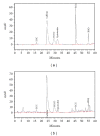
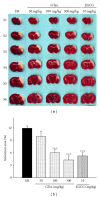
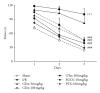
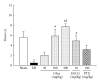
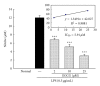
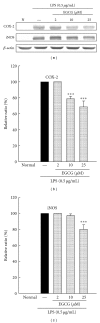
Ischemic stroke results in brain damage and behavioral deficits including memory impairment. Protective effects of green tea extract (GTex) and its major functional polyphenol (-)-epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) on memory were examined in cerebral ischemic rats. GTex and EGCG were administered 1 hr before middle cerebral artery ligation in rats. GTex, EGCG, and pentoxifylline (PTX) significantly improved ishemic-induced memory impairment in a Morris water maze test. Malondialdehyde (MDA) levels, glutathione (GSH), and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus were increased by long-term treatment with GTex and EGCG. Both compounds were also associated with reduced cerebral infraction breakdown of MDA and GSH in the hippocampus. In in vitro experiments, EGCG had anti-inflammatory effects in BV-2 microglia cells. EGCG inhibited lipopolysaccharide- (LPS-) induced nitric oxide production and reduced cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in BV-2 cells. GTex and its active polyphenol EGCG improved learning and memory deficits in a cerebral ischemia animal model and such protection may be due to the reduction of oxidative stress and neuroinflammation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chronic epigallocatechin-3-gallate ameliorates learning and memory deficits in diabetic rats via modulation of nitric oxide and oxidative stress.Behav Brain Res. 2011 Oct 31;224(2):305-10. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2011.06.007. Epub 2011 Jun 14. Behav Brain Res. 2011. PMID: 21699923
-
Anti-Amnesic Effects of Epigallocatechin Gallate on Scopolamine-Induced Learning and Memory Dysfunction in Sprague-Dawley Rats.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Dec 21;11(1):1. doi: 10.3390/antiox11010001. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35052505 Free PMC article.
-
Nitric oxide pathway activity modulation alters the protective effects of (-)Epigallocatechin-3-gallate on reserpine-induced impairment in rats.Behav Brain Res. 2016 May 15;305:198-211. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2016.02.038. Epub 2016 Mar 2. Behav Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 26944334
-
Green Tea Polyphenol (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG): A Time for a New Player in the Treatment of Respiratory Diseases?Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Aug 13;11(8):1566. doi: 10.3390/antiox11081566. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36009285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Green tea polyphenols as an anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory agent for cardiovascular protection.Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2007 Jun;7(2):135-44. doi: 10.2174/187152907780830905. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2007. PMID: 17584048 Review.
Cited by
-
Epigallocatechin gallate improves neuronal damage in animal model of ischemic stroke and glutamate-exposed neurons via modulation of hippocalcin expression.PLoS One. 2024 Mar 1;19(3):e0299042. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0299042. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38427657 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Polyphenols as Antioxidant Supplementation in Ischemic Stroke.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Jun 25;2021:5471347. doi: 10.1155/2021/5471347. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 34257802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Green Tea Catechins Attenuate Neurodegenerative Diseases and Cognitive Deficits.Molecules. 2022 Nov 6;27(21):7604. doi: 10.3390/molecules27217604. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36364431 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of gallic acid on chronic restraint stress-induced anxiety and memory loss in male BALB/c mice.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2018 Dec;21(12):1232-1237. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2018.31230.7523. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 30627366 Free PMC article.
-
Green tea catechins inhibit microglial activation which prevents the development of neurological disorders.Neural Regen Res. 2020 Oct;15(10):1792-1798. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.280300. Neural Regen Res. 2020. PMID: 32246619 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lo EH, Dalkara T, Moskowitz MA. Mechanisms, challenges and opportunities in stroke. Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 2003;4(5):399–415. - PubMed
-
- Xiang J, Tang YP, Wu P, Gao JP, Cai DF. Chinese medicine Nao-Shuan-Tong attenuates cerebral ischemic injury by inhibiting apoptosis in a rat model of stroke. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2010;131(1):174–181. - PubMed
-
- Yanpallewar SU, Hota D, Rai S, Kumar M, Acharya SB. Nimodipine attenuates biochemical, behavioral and histopathological alterations induced by acute transient and long-term bilateral common carotid occlusion in rats. Pharmacological Research. 2004;49(2):143–150. - PubMed
-
- McCord JM. Oxygen-derived free radicals in postischemic tissue injury. The New England Journal of Medicine. 1985;312(3):159–163. - PubMed
-
- Macdonald RL, Stoodley M. Pathophysiology of cerebral ischemia. Neurologia Medico-Chirurgica. 1998;38(1):1–11. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

