Thyroid and Hepatic Haemodynamic Alterations among Egyptian Children with Liver Cirrhosis
- PMID: 22919507
- PMCID: PMC3419423
- DOI: 10.5402/2012/595734
Thyroid and Hepatic Haemodynamic Alterations among Egyptian Children with Liver Cirrhosis
Abstract
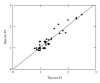
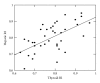
Background. Alterations in thyroid hormones regulation and metabolism are frequently observed in patients with cirrhosis. Aims. To assess alterations in thyroid volume (TV), haemodynamics, and hormones in patients with cirrhosis and their relation to hepatic arterial haemodynamics, and disease severity. Methods. Forty cirrhotic patients were compared to 30 healthy subjects regarding TV, free triiodiothyronine (fT(3)), free tetraiodothyronine (fT(4)), thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), and pulsatility and resistance indices in the inferior thyroid and hepatic arteries. Results. TV (P = 0.042), thyroid volume standard deviation score (TVSDS, P = 0.001), Inferior Thyroid Artery Pulsatility Index (ITAPI, P = 0.001), Inferior Thyroid Artery Resistance Index (ITARI, P = 0.041), Hepatic Artery Pulsatility Index (HAPI, P = 0.029) and Hepatic Artery Resistance Index (HARI, P = 0.035) were higher among cases being highest in Child-C patients. FT(3) was lower in patients than controls (P = 0.001) and correlated negatively with ITAPI (r = -0.71, P = 0.021) and ITARI (r = -0.79, P = 0.011). ITAPI and ITARI correlated directly with HAPI and HARI (r = 0.62, P = 0.03, and r = 0.42, P = 0.04, resp.). Conclusions. Thyroid is involved in the haemodynamic alterations of cirrhosis. Routine study of thyroid by Doppler and assessment of thyroid functions should be performed in patients with cirrhosis to offer proper treatment if needed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Alterations in thyroid Doppler arterial resistance indices, volume and hormones in cirrhosis: relationships with splanchnic haemodynamics.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2004 Jan;30(1):19-25. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2003.10.008. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2004. PMID: 14962604
-
Is non-invasive diagnosis of esophageal varices in patients with compensated hepatic cirrhosis possible by duplex Doppler ultrasonography?Indian J Gastroenterol. 2016 Jan;35(1):60-6. doi: 10.1007/s12664-016-0630-7. Epub 2016 Feb 29. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 26923375
-
Assessment of Portal Venous and Hepatic Artery Haemodynamic Variation in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Patients.J Clin Diagn Res. 2016 Aug;10(8):TC07-10. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2016/20697.8267. Epub 2016 Aug 1. J Clin Diagn Res. 2016. PMID: 27656524 Free PMC article.
-
Hemodynamic features of Doppler ultrasonography in patients with portal hypertension: intraoperative direct measurement of portal pressure in the portal venous system.J Ultrasound Med. 2007 Dec;26(12):1689-96. doi: 10.7863/jum.2007.26.12.1689. J Ultrasound Med. 2007. PMID: 18029920 Clinical Trial.
-
The value of Doppler ultrasound in cirrhosis and portal hypertension.Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1999;230:82-8. doi: 10.1080/003655299750025598. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1999. PMID: 10499467 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of Thyroid Function Tests in Children with Chronic Liver Diseases.J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2020 Jun 3;12(2):143-149. doi: 10.4274/jcrpe.galenos.2019.2019.0029. Epub 2019 Sep 5. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 31486329 Free PMC article.
-
The Clinical Value of Thyroid Hormone Levels and Correlation with Severity of Liver Cirrhosis.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022 Jun 6;2022:5365172. doi: 10.1155/2022/5365172. eCollection 2022. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Intell Neurosci. 2023 Jul 19;2023:9873614. doi: 10.1155/2023/9873614. PMID: 35707192 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Vitamin D and chronic hepatitis C: effects on success rate and prevention of side effects associated with pegylated interferon-α and ribavirin.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Jul 15;8(7):10284-303. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26379820 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Friedman SL. The cellular basis of hepatic fibrosis—mechanisms and treatment strategies. The New England Journal of Medicine. 1993;328(25):1828–1835. - PubMed
-
- Groszmann RJ. Hyperdynamic circulation of liver disease 40 years later: pathophysiology and clinical consequences. Hepatology. 1994;20(5):1359–1363. - PubMed
-
- Langer DA, Shah VH. Nitric oxide and portal hypertension: interface of vasoreactivity and angiogenesis. Journal of Hepatology. 2006;44(1):209–216. - PubMed
-
- Sabba C, Ferraioli G, Genecin P, et al. Evaluation of postprandial hyperemia in superior mesenteric artery and portal vein in healthy and cirrhotic humans: an operator-blind echo-Doppler study. Hepatology. 1991;13(4):714–718. - PubMed
-
- Fernandez-Sear J, Prieto J, Quiroga J, et al. Systemic and regional hemodynamics in patients with liver cirrhosis and ascites with and without functional renal failure. Gastroenterology. 1989;97(5):1304–1312. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources