Staphylococcus aureus hemolysins, bi-component leukocidins, and cytolytic peptides: a redundant arsenal of membrane-damaging virulence factors?
- PMID: 22919604
- PMCID: PMC3417661
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2012.00012
Staphylococcus aureus hemolysins, bi-component leukocidins, and cytolytic peptides: a redundant arsenal of membrane-damaging virulence factors?
Abstract
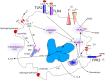
One key aspect of the virulence of Staphylococcus aureus lies in its ability to target the host cell membrane with a large number of membrane-damaging toxins and peptides. In this review, we describe the hemolysins, the bi-component leukocidins (which include the Panton Valentine leukocidin, LukAB/GH, and LukED), and the cytolytic peptides (phenol soluble modulins). While at first glance, all of these factors might appear redundant, it is now clear that some of these factors play specific roles in certain S. aureus life stages and diseases or target specific cell types or species. In this review, we present an update of the literature on toxin receptors and their cell type and species specificities. Furthermore, we review epidemiological studies and animal models illustrating the role of these membrane-damaging factors in various diseases. Finally, we emphasize the interplay of these factors with the host immune system and highlight all their non-lytic functions.
Keywords: PSM; Panton Valentine leukocidin; Staphylococcus aureus; hemolysin; inflammasome; leukocidin; neutrophil; pore-forming toxin.
Figures

References
-
- Alonzo Iii F., Benson M. A., Chen J., Novick R. P., Shopsin B., Torres V. J. (2012). Staphylococcus aureus leukocidin ED contributes to systemic infection by targeting neutrophils and promoting bacterial growth in vivo. Mol. Microbiol. 83, 423–43510.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07942.x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bae I. G., Tonthat G. T., Stryjewski M. E., Rude T. H., Reilly L. F., Barriere S. L., Genter F. C., Corey G. R., Fowler V. G., Jr. (2009). Presence of genes encoding the panton-valentine leukocidin exotoxin is not the primary determinant of outcome in patients with complicated skin and skin structure infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: results of a multinational trial. J. Clin. Microbiol. 47, 3952–395710.1128/JCM.01643-09 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bantel H., Sinha B., Domschke W., Peters G., Schulze-Osthoff K., Janicke R. U. (2001). alpha-Toxin is a mediator of Staphylococcus aureus-induced cell death and activates caspases via the intrinsic death pathway independently of death receptor signaling. J. Cell Biol. 155, 637–64810.1083/jcb.200105081 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bayer A. S., Ramos M. D., Menzies B. E., Yeaman M. R., Shen A. J., Cheung A. L. (1997). Hyperproduction of alpha-toxin by Staphylococcus aureus results in paradoxically reduced virulence in experimental endocarditis: a host defense role for platelet microbicidal proteins. Infect. Immun. 65, 4652–4660 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

