An RGD helper sequence in CagL of Helicobacter pylori assists in interactions with integrins and injection of CagA
- PMID: 22919661
- PMCID: PMC3417467
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2012.00070
An RGD helper sequence in CagL of Helicobacter pylori assists in interactions with integrins and injection of CagA
Abstract
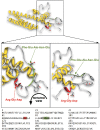
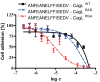
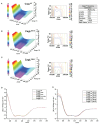
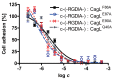
Helicobacter pylori is a specific gastric pathogen that colonizes the stomach in more than 50% of the world's human population. Infection with this bacterium can induce several types of gastric pathology, ranging from chronic gastritis to peptic ulcers and even adenocarcinoma. Virulent H. pylori isolates encode components of a type IV secretion system (T4SS), which form a pilus for the injection of virulence proteins such as CagA into host target cells. This is accomplished by a specialized adhesin on the pilus surface, the protein CagL, a putative VirB5 ortholog, which binds to host cell β(1) integrin, triggering subsequent delivery of CagA across the host cell membrane. Like the human extracellular matrix protein fibronectin, CagL contains an RGD (Arg-Gly-Asp) motif and is able to trigger intracellular signaling pathways by RGD-dependent binding to integrins. While CagL binding to host cells is mediated primarily by the RGD motif, we identified an auxiliary binding motif for CagL-integrin interaction. Here, we report on a surface exposed FEANE (Phe-Glu-Ala-Asn-Glu) interaction motif in spatial proximity to the RGD sequence, which enhances the interactions of CagL with integrins. It will be referred to as RGD helper sequence (RHS). Competitive cell adhesion assays with recombinant wild type CagL and point mutants, competition experiments with synthetic cyclic and linear peptides, and peptide array experiments revealed amino acids essential for the interaction of the RHS motif with integrins. Infection experiments indicate that the RHS motif plays a role in the early interaction of H. pylori T4SS with integrin, to trigger signaling and to inject CagA into host cells. We thus postulate that CagL is a versatile T4SS surface protein equipped with at least two motifs to promote binding to integrins, thereby causing aberrant signaling within host cells and facilitating translocation of CagA into host cells, thus contributing directly to H. pylori pathogenesis.
Keywords: CagL; ERK kinase; binding motifs; cortactin; integrin interaction; α5β1.
Figures
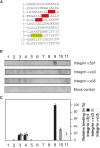
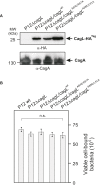
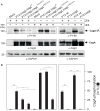
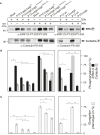
Similar articles
-
Specific high affinity interaction of Helicobacter pylori CagL with integrin αV β6 promotes type IV secretion of CagA into human cells.FEBS J. 2019 Oct;286(20):3980-3997. doi: 10.1111/febs.14962. Epub 2019 Jun 27. FEBS J. 2019. PMID: 31197920
-
A novel NOD1- and CagA-independent pathway of interleukin-8 induction mediated by the Helicobacter pylori type IV secretion system.Cell Microbiol. 2013 Apr;15(4):554-70. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12055. Epub 2012 Nov 21. Cell Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23107019
-
Helicobacter pylori exploits a unique repertoire of type IV secretion system components for pilus assembly at the bacteria-host cell interface.PLoS Pathog. 2011 Sep;7(9):e1002237. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002237. Epub 2011 Sep 1. PLoS Pathog. 2011. PMID: 21909278 Free PMC article.
-
Role of type IV secretion in Helicobacter pylori pathogenesis.Cell Microbiol. 2008 Aug;10(8):1573-81. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2008.01156.x. Epub 2008 Apr 8. Cell Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18410539 Review.
-
Type IV Secretion and Signal Transduction of Helicobacter pylori CagA through Interactions with Host Cell Receptors.Toxins (Basel). 2017 Mar 24;9(4):115. doi: 10.3390/toxins9040115. Toxins (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28338646 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CagL polymorphisms between East Asian and Western Helicobacter pylori are associated with different abilities to induce IL-8 secretion.J Microbiol. 2021 Aug;59(8):763-770. doi: 10.1007/s12275-021-1136-2. Epub 2021 Jun 1. J Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34061339
-
Tailor-Made Detection of Individual Phosphorylated and Non-Phosphorylated EPIYA-Motifs of Helicobacter pylori Oncoprotein CagA.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Aug 13;11(8):1163. doi: 10.3390/cancers11081163. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31412675 Free PMC article.
-
Helicobacter pylori CagL Y58/E59 mutation turns-off type IV secretion-dependent delivery of CagA into host cells.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 3;9(6):e97782. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097782. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24893039 Free PMC article.
-
Helicobacter pylori CagA Induces Cortactin Y-470 Phosphorylation-Dependent Gastric Epithelial Cell Scattering via Abl, Vav2 and Rac1 Activation.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Aug 23;13(16):4241. doi: 10.3390/cancers13164241. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34439396 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial thiol oxidoreductases - from basic research to new antibacterial strategies.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017 May;101(10):3977-3989. doi: 10.1007/s00253-017-8291-8. Epub 2017 Apr 13. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28409380 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aota S., Nomizu M., Yamada K. M. (1994). The short amino acid sequence Pro-His-Ser-Arg-Asn in human fibronectin enhances cell adhesive function. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 24756–24761 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

