Detection of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli by sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using chicken egg yolk IgY antibodies
- PMID: 22919675
- PMCID: PMC3417390
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2012.00084
Detection of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli by sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using chicken egg yolk IgY antibodies
Abstract
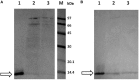
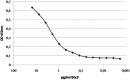
Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC), a subset of Shiga toxin producing E. coli (STEC) is associated with a spectrum of diseases that includes diarrhea, hemorrhagic colitis and a life-threatening hemolytic-uremic syndrome (HUS). Regardless of serotype, Shiga toxins (Stx1 and/or Stx2) are uniformly expressed by all EHEC, and so exploitable targets for laboratory diagnosis of these pathogens. In this study, a sandwich ELISA for determination of Shiga toxin (Stx) was developed using anti-Stx2B subunit antibodies and its performance was compared with that of the Vero cell assay and a commercial immunoassay kit. Chicken IgY was used as capture antibody and a HRP-conjugated rabbit IgG as the detection antibody. The anti-Stx2B IgY was harvested from eggs laid by hens immunized with a recombinant protein fragment. Several parameters were tested in order to optimize the sandwich ELISA assay, including concentration of antibodies, type and concentration of blocking agent, and incubation temperatures. Supernatants from 42 STEC strains of different serotypes and stx variants, including stx(2EDL933), stx(2vha), stx(2vhb), stx(2g), stx(1EDL933), and stx(1d) were tested. All Stx variants were detected by the sandwich ELISA, with a detection limit of 115 ng/ml Stx2. Twenty three strains negative for stx genes, including different bacteria species, showed no activity in Vero cell assay and produced negative results in ELISA, except for two strains. Our results show that anti-Stx2B IgY sandwich ELISA could be used in routine diagnosis as a rapid, specific and economic method for detection of Shiga toxin-producing E. coli.
Keywords: ELISA; Escherichia coli; IgY; STEC; Shiga toxin; chicken; egg yolk.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Development and Evaluation of a Novel VHH-Based Immunocapture Assay for High-Sensitivity Detection of Shiga Toxin Type 2 (Stx2) in Stool Samples.J Clin Microbiol. 2020 Feb 24;58(3):e01566-19. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01566-19. Print 2020 Feb 24. J Clin Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31826960 Free PMC article.
-
Antibodies anti-Shiga toxin 2 B subunit from chicken egg yolk: isolation, purification and neutralization efficacy.Toxicon. 2011 Sep 15;58(4):380-8. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2011.07.009. Epub 2011 Jul 22. Toxicon. 2011. PMID: 21803069 Free PMC article.
-
Production and characterization of rabbit polyclonal sera against Shiga toxins Stx1 and Stx2 for detection of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli.Microbiol Immunol. 2008 Oct;52(10):484-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.2008.00068.x. Microbiol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18822082
-
New Therapeutic Developments against Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli.Microbiol Spectr. 2014 Oct;2(5). doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.EHEC-0013-2013. Microbiol Spectr. 2014. PMID: 26104346 Review.
-
Pathogenic Factors and Recent Study on the Rapid Detection of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli (STEC).Mol Biotechnol. 2025 Jan;67(1):16-26. doi: 10.1007/s12033-023-00985-8. Epub 2023 Dec 28. Mol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 38153662 Review.
Cited by
-
Production of egg yolk antibody (IgY) against a chimeric protein containing IpaD, StxB, and TolC antigens from Shigella: An investigation of its prophylactic effects against Shiga toxin (Stx) and Shigella dysenteriae in vitro and in vivo.Heliyon. 2024 Feb 16;10(4):e26361. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26361. eCollection 2024 Feb 29. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38404796 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous Detection of Three Foodborne Pathogens Based on Immunomagnetic Nanoparticles and Fluorescent Quantum Dots.ACS Omega. 2020 Sep 3;5(36):23070-23080. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c02833. eCollection 2020 Sep 15. ACS Omega. 2020. PMID: 32954157 Free PMC article.
-
Shiga-Like Toxin Produced by Local Isolates of Escherichia coli O157:H7 Induces Apoptosis of the T47 Breast Cancer Cell Line.Breast Cancer (Auckl). 2021 Apr 28;15:11782234211010120. doi: 10.1177/11782234211010120. eCollection 2021. Breast Cancer (Auckl). 2021. PMID: 35173438 Free PMC article.
-
Bacteriological assessments of foodborne pathogens in poultry meat at different super shops in Dhaka, Bangladesh.Ital J Food Saf. 2019 Mar 26;8(1):6720. doi: 10.4081/ijfs.2019.6720. eCollection 2019 Mar 18. Ital J Food Saf. 2019. PMID: 31008079 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoglobulin Y for Potential Diagnostic and Therapeutic Applications in Infectious Diseases.Front Immunol. 2021 Jun 9;12:696003. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.696003. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34177963 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Azim T., Ronan A., Khan W. A., Salam M. A., Albert M. J., Bennish M. L. (1997). “Features of Shigella-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) in children, abstr. V187/I,” in Third International Symposium and Workshop on Shiga Toxin (Verotoxin)-Producing Escherichia coli Infections (Melville, NY: Lois Joy Galler Foundation for Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome Inc.), 22
-
- Ball H. J., Finlay D., Zafar A., Wilson T. (1996). The detection of verocytotoxins in bacterial cultures from human diarrhoeal samples with monoclonal antibody-based ELISAs. J. Med. Microbiol. 44, 273–276 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

