In vitro glucocorticoid sensitivity is associated with clinical glucocorticoid therapy outcome in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 22920577
- PMCID: PMC3580593
- DOI: 10.1186/ar4029
In vitro glucocorticoid sensitivity is associated with clinical glucocorticoid therapy outcome in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Introduction: Genetic and disease-related factors give rise to a wide spectrum of glucocorticoid (GC) sensitivity in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). In clinical practice, GC treatment is not adapted to these differences in GC sensitivity. In vitro assessment of GC sensitivity before the start of therapy could allow more individualized GC therapy. The aim of the study was to investigate the association between in vitro and in vivo GC sensitivity in RA.
Methods: Thirty-eight early and 37 established RA patients were prospectively studied. In vitro GC sensitivity was assessed with dexamethasone-induced effects on interleukin-2 (IL-2) and glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper (GILZ) messenger RNA expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). A whole-cell dexamethasone-binding assay was used to measure number and affinity (1/KD) of glucocorticoid receptors (GRs).
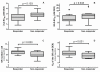
Results: GR number was positively correlated with improvement in DAS. IL-2-EC₅₀ and GILZ-EC₅₀ values both had weak near-significant correlations with clinical improvement in DAS in intramuscularly treated patients only. HAQ responders had lower GILZ-EC₅₀ values and higher GR number and KD.
Conclusions: Baseline cellular in vitro glucocorticoid sensitivity is modestly associated with in vivo improvement in DAS and HAQ-DI score after GC bridging therapy in RA. Further studies are needed to evaluate whether in vitro GC sensitivity may support the development of tailor-made GC therapy in RA.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Polymorphisms in the glucocorticoid receptor gene and in the glucocorticoid-induced transcript 1 gene are associated with disease activity and response to glucocorticoid bridging therapy in rheumatoid arthritis.Rheumatol Int. 2015 Aug;35(8):1325-33. doi: 10.1007/s00296-015-3235-z. Epub 2015 Feb 28. Rheumatol Int. 2015. PMID: 25724472 Free PMC article.
-
Does addition of glucocorticoids to the initial therapy influence the later course of the disease in patients with early RA? Results from the Swiss prospective observational registry (SCQM).Clin Rheumatol. 2017 Jan;36(1):59-66. doi: 10.1007/s10067-016-3468-6. Epub 2016 Nov 12. Clin Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 27838788
-
Role of mRNA expression of transcription factors in glucocorticoid sensitivity of peripheral blood mononuclear cells and disease state in rheumatoid arthritis.J Rheumatol. 2004 Mar;31(3):464-9. J Rheumatol. 2004. PMID: 14994389
-
Role of GILZ in immune regulation, glucocorticoid actions and rheumatoid arthritis.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011 Jun;7(6):340-8. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2011.59. Epub 2011 May 10. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011. PMID: 21556028 Review.
-
Controversies in rheumatoid arthritis glucocorticoid therapy.Joint Bone Spine. 2018 Jul;85(4):417-422. doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2017.12.002. Epub 2017 Dec 12. Joint Bone Spine. 2018. PMID: 29246530 Review.
Cited by
-
Vitamin D interferes with glucocorticoid responsiveness in human peripheral blood mononuclear target cells.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016 Nov;73(22):4341-4354. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2281-3. Epub 2016 May 24. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 27220430 Free PMC article.
-
CIRMI-a new term for a concept worthy of further exploration: a narrative review.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Jun;10(11):646. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-5572. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35813323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A focused Real Time PCR strategy to determine GILZ expression in mouse tissues.Results Immunol. 2015 Oct 21;5:37-42. doi: 10.1016/j.rinim.2015.10.003. eCollection 2015. Results Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26697291 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoid sensitivity in Behçet's disease.Endocr Connect. 2012 Oct 24;1(2):103-11. doi: 10.1530/EC-12-0056. Print 2012 Nov 1. Endocr Connect. 2012. PMID: 23781311 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of the Type I Interferon Response During Immunosuppressive Therapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Front Immunol. 2019 Apr 24;10:902. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00902. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31068954 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van Schaardenburg D, Valkema R, Dijkmans BA, Papapoulos S, Zwinderman AH, Han KH, Pauwels EK, Breedveld FC. Prednisone treatment of elderly-onset rheumatoid arthritis: disease activity and bone mass in comparison with chloroquine treatment. Arthritis Rheum. 1995;38:334–342. doi: 10.1002/art.1780380307. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sliwinska-Stanczyk P, Pazdur J, Ziolkowska M, Jaworski J, Kaminska-Tchorzewska E, Lacki JK. The effect of methylprednisolone on proliferation of PBMCs obtained from steroid-sensitive and steroid-resistant rheumatoid arthritis patients. Scand J Rheumatol. 2007;36:167–171. doi: 10.1080/03009740601154111. - DOI - PubMed
-
- van Oosten MJ, Dolhain RJ, Koper JW, van Rossum EF, Emonts M, Han KH, Wouters JM, Hazes JM, Lamberts SW, Feelders RA. Polymorphisms in the glucocorticoid receptor gene that modulate glucocorticoid sensitivity are associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12:R159. doi: 10.1186/ar3118. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

