Releasable layer-by-layer assembly of stabilized lipid nanocapsules on microneedles for enhanced transcutaneous vaccine delivery
- PMID: 22920601
- PMCID: PMC3475723
- DOI: 10.1021/nn302639r
Releasable layer-by-layer assembly of stabilized lipid nanocapsules on microneedles for enhanced transcutaneous vaccine delivery
Abstract
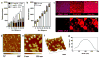
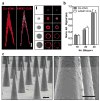
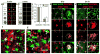
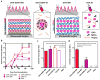
Here we introduce a new approach for transcutaneous drug delivery, using microneedles coated with stabilized lipid nanocapsules, for delivery of a model vaccine formulation. Poly(lactide-co-glycolide) microneedle arrays were coated with multilayer films via layer-by-layer assembly of a biodegradable cationic poly(β-amino ester) (PBAE) and negatively charged interbilayer-cross-linked multilamellar lipid vesicles (ICMVs). To test the potential of these nanocapsule-coated microneedles for vaccine delivery, we loaded ICMVs with a protein antigen and the molecular adjuvant monophosphoryl lipid A. Following application of microneedle arrays to the skin of mice for 5 min, (PBAE/ICMV) films were rapidly transferred from microneedle surfaces into the cutaneous tissue and remained in the skin following removal of the microneedle arrays. Multilayer films implanted in the skin dispersed ICMV cargos in the treated tissue over the course of 24 h in vivo, allowing for uptake of the lipid nanocapsules by antigen presenting cells in the local tissue and triggering their activation in situ. Microneedle-mediated transcutaneous vaccination with ICMV-carrying multilayers promoted robust antigen-specific humoral immune responses with a balanced generation of multiple IgG isotypes, whereas bolus delivery of soluble or vesicle-loaded antigen via intradermal injection or transcutaneous vaccination with microneedles encapsulating soluble protein elicited weak, IgG(1)-biased humoral immune responses. These results highlight the potential of lipid nanocapsules delivered by microneedles as a promising platform for noninvasive vaccine delivery applications.
Figures


References
-
- DeVilliers MM, Otto DP, Strydom SJ, Lvov YM. Introduction to Nanocoatings Produced by Layer-by-Layer (LbL) Self-Assembly. Adv Drug Delivery Rev. 2011;63:701–715. - PubMed
-
- Hammond PT. Engineering Materials Layer-by-Layer: Challenges and Apportunities in Multilayer Assembly. AIChE J. 2011;57:2928–2940.
-
- Katagiri K, Hamasaki R, Ariga K, Kikuchi J-i. Layered Paving of Vesicular Nanoparticles Formed with Cerasome as a Bioinspired Organic-Inorganic Hybrid. J Am Chem Soc. 2002;124:7892–7893. - PubMed
-
- Katagiri K, Hamasaki R, Ariga K, Kikuchi J-i. Layer-by-Layer Self-Assembling of Liposomal Nanohybrid “Cerasome” on Substrates. Langmuir. 2002;18:6709–6711.
-
- Graf N, Tanno A, Dochter A, Rothfuchs N, Voeroes J, Zambelli T. Electrochemically Driven delivery to Cells from Vesicles Embedded in Polyelectrolyte Multilayers. Soft Matter. 2012;8:3641–3648.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

