Comparison of patient preference for two insulin injection pen devices in relation to patient dexterity skills
- PMID: 22920818
- PMCID: PMC3440163
- DOI: 10.1177/193229681200600423
Comparison of patient preference for two insulin injection pen devices in relation to patient dexterity skills
Abstract
Background: Impaired dexterity has been reported to be prevalent in diabetes patients independent from the existence of diabetic neuropathy. This study was performed to investigate the impact of dexterity impairment on patient preference for two insulin pen injection devices (InnoLet and FlexTouch).
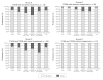
Methods: Ninety patients [54 male/36 female; age (mean ± standard deviation), 62 ± 8 years; disease duration, 18 ± 11 years; hemoglobin A1c, 7.2 ± 1.0%] were included in this investigation and were stratified into four different groups based on the results of a dexterity test (Jebsen-Taylor Hand Function Test) and assessment of visual impairment: 15 type 1 (group A) and 30 type 2 (group B) patients with impaired dexterity, 30 type 1/type 2 patients with visual impairment (group C), and 15 type 1/type 2 patients without any impairment (group D). The patients performed a cognitive function test (number connection test), were introduced to the devices in random order, and were asked to perform some mock injections before completing a six-item standardized preference questionnaire.
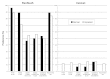
Results: There was a strong preference for FlexTouch in all groups. All unimpaired patients (100%, group D) preferred FlexTouch, as did the vast majority in all other groups. Only 11% of the patients with impaired cognitive function preferred InnoLet, as did a few patients with more severely impaired dexterity or with visual impairment (group A, 13%; group B, 3%; group C, 14%).
Conclusions: Patient dexterity skills may have an influence on device preference, especially if the impairment is more pronounced.
© 2012 Diabetes Technology Society.
Figures
Comment in
-
Analysis of comparison of patient preference for two insulin injection pen devices in relation to patient dexterity skills.J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2012 Jul 1;6(4):917-20. doi: 10.1177/193229681200600424. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2012. PMID: 22920819 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ignaut DA, Schwartz SL, Sarwat S, Murphy HL. Comparative device assessments: Humalog KwikPen compared with vial and syringe and FlexPen. Diabetes Educ. 2009;35(5):789–798. - PubMed
-
- Clark PE, Valentine V, Bodie JN, Sarwat S. Ease of use and patient preference injection simulation study comparing two prefilled insulin pens. Curr Med Res Opin. 2010;26(7):1745–1753. - PubMed
-
- Pfützner A. FlexPen for the delivery of insulin: accuracy, injection force and patient preference. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2009;6(2):115–123. - PubMed
-
- Bailey T, Thurman J, Niemeyer M, Schmeisl G. Usability and preference evaluation of a prefilled insulin pen with a novel injection mechanism by people with diabetes and healthcare professionals. Curr Med Res Opin. 2011;27(10):2043–2052. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

