The therapeutic target Hsp90 and cancer hallmarks
- PMID: 22920906
- PMCID: PMC7553218
- DOI: 10.2174/138161213804143725
The therapeutic target Hsp90 and cancer hallmarks
Abstract
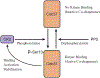
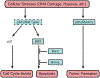
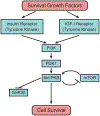
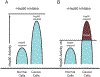
Hsp90 is a major molecular chaperone that is expressed abundantly and plays a pivotal role in assisting correct folding and functionality of its client proteins in cells. The Hsp90 client proteins include a wide variety of signal transducing molecules such as protein kinases and steroid hormone receptors. Cancer is a complex disease, but most types of human cancer share common hallmarks, including self-sufficiency in growth signals, insensitivity to growth-inhibitory mechanism, evasion of programmed cell death, limitless replicative potential, sustained angiogenesis, and tissue invasion and metastasis. A surprisingly large number of Hsp90-client proteins play crucial roles in establishing cancer cell hallmarks. We start the review by describing the structure and function of Hsp90 since conformational changes during the ATPase cycle of Hsp90 are closely related to its function. Many co-chaperones, including Hop, p23, Cdc37, Aha1, and PP5, work together with Hsp90 by modulating the chaperone machinery. Post-translational modifications of Hsp90 and its cochaperones are vital for their function. Many tumor-related Hsp90-client proteins, including signaling kinases, steroid hormone receptors, p53, and telomerase, are described. Hsp90 and its co-chaperones are required for the function of these tumor-promoting client proteins; therefore, inhibition of Hsp90 by specific inhibitors such as geldanamycin and its derivatives attenuates the tumor progression. Hsp90 inhibitors can be potential and effective cancer chemotherapeutic drugs with a unique profile and have been examined in clinical trials. We describe possible mechanisms why Hsp90 inhibitors show selectivity to cancer cells even though Hsp90 is essential also for normal cells. Finally, we discuss the "Hsp90-addiction" of cancer cells, and suggest a role for Hsp90 in tumor evolution.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors confirm that this article content has no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Csermely P, Schnaider T, Söti C, Prohászka Z, Nardai G. The 90-kDa molecular chaperone family: structure, function, and clinical applications. A comprehensive review. Pharmacol Ther 1998; 79: 129–68. - PubMed
-
- Felts SJ, Owen BA, Nguyen P, Trepel J, Donner DB, Toft DO. The hsp90-related protein TRAP1 is a mitochondrial protein with distinct functional properties. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 3305–12. - PubMed
-
- Schmitz G, Schmidt M, Feierabend J. Characterization of a plastid-specific HSP90 homologue: identification of a cDNA sequence, phylogenetic descendence and analysis of its mRNA and protein expression. Plant Mol Biol 1996; 30: 479–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

