Regulation of humoral immunity by complement
- PMID: 22921118
- PMCID: PMC5784422
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.08.002
Regulation of humoral immunity by complement
Abstract
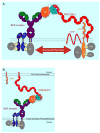
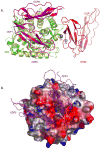
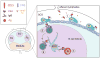
The complement system of innate immunity is important in regulating humoral immunity largely through the complement receptor CR2, which forms a coreceptor on B cells during antigen-induced activation. However, CR2 also retains antigens on follicular dendritic cells (FDCs). Display of antigen on FDCs is critical for clonal selection and affinity maturation of activated B cells. This review will discuss the role of complement in adaptive immunity in general with a focus on the interplay between CR2-associated antigen on B cells with CR2 expressed on FDCs. This latter interaction provides an opportunity for memory B cells to sample antigen over prolonged periods. The cocrystal structure of CR2 with its ligand C3d provides insight into how the complement system regulates access of antigen by B cells with implications for therapeutic manipulations to modulate aberrant B cell responses in the case of autoimmunity.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
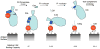
References
-
- Barrault DV, Steward M, Cox VF, Smith RA, Knight AM. Efficient production of complement (C3d)3 fusion proteins using the baculovirus expression vector system. J Immunol Methods. 2005;304:158–173. - PubMed
-
- Boes M, Esau C, Fischer MB, Schmidt T, Carroll M, Chen J. Enhanced B-1 cell development, but impaired IgG antibody responses in mice deficient in secreted IgM. J Immunol. 1998;160:4776–4787. - PubMed
-
- Burman JD, Leung E, Atkins KL, O’Seaghdha MN, Lango L, Bernado P, Bagby S, Svergun DI, Foster TJ, Isenman DE, van den Elsen JM. Interaction of human complement with Sbi, a staphylococcal immunoglobulin-binding protein: indications of a novel mechanism of complement evasion by Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:17579–17593. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

