Identification of cytoplasmic capping targets reveals a role for cap homeostasis in translation and mRNA stability
- PMID: 22921400
- PMCID: PMC3462258
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2012.07.011
Identification of cytoplasmic capping targets reveals a role for cap homeostasis in translation and mRNA stability
Abstract
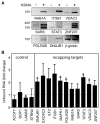
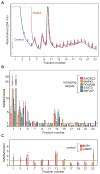
The notion that decapping leads irreversibly to messenger RNA (mRNA) decay was contradicted by the identification of capped transcripts missing portions of their 5' ends and a cytoplasmic complex that can restore the cap on uncapped mRNAs. In this study, we used accumulation of uncapped transcripts in cells inhibited for cytoplasmic capping to identify the targets of this pathway. Inhibition of cytoplasmic capping results in the destabilization of some transcripts and the redistribution of others from polysomes to nontranslating messenger ribonucleoproteins, where they accumulate in an uncapped state. Only a portion of the mRNA transcriptome is affected by cytoplasmic capping, and its targets encode proteins involved in nucleotide binding, RNA and protein localization, and the mitotic cell cycle. The 3' untranslated regions of recapping targets are enriched for AU-rich elements and microRNA binding sites, both of which function in cap-dependent mRNA silencing. These findings identify a cyclical process of decapping and recapping that we term cap homeostasis.
Copyright © 2012 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Anderson P, Kedersha N. Stressful initiations. J Cell Sci. 2002;115:3227–3234. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

