A combination of increased Rho kinase activity and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide predicts worse cardiovascular outcome in patients with acute coronary syndrome
- PMID: 22921817
- PMCID: PMC3807084
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2012.07.007
A combination of increased Rho kinase activity and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide predicts worse cardiovascular outcome in patients with acute coronary syndrome
Abstract
Background: Recent experimental evidence suggests that the Rho/Rho-kinase (ROCK) system may play an important role in the pathogenesis of acute coronary syndrome (ACS) but there are little clinical data. This study examined if ROCK activity is increased in patients with acute coronary syndrome and if ROCK activity predicts long-term cardiovascular event.
Method: Blood samples were collected from 188 patients within 12h after admission for ACS (53% men; aged 70 ± 13) and from 61 control subject. The main outcome measures were all cause mortality, readmission with ACS or congestive heart failure (CHF) from presentation within around 2 years (mean:14.4 ± 7.2 months; range: 0.5 to 26 months).
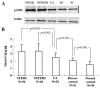
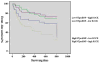
Results: ROCK activity increased in ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI, n=90) (3.33 ± 0.93), non-STEMI (NSTEMI, n=68) (3.37 ± 1.04) and unstable angina (UA, n=30) (2.53 ± 0.59) groups when compared with disease controls (n=31) (2.06 ± 0.38, all p<0.001) and healthy controls (n=30) (1.54 ± 0.43, all p<0.001). There were 24 deaths, 34 readmissions with ACS and 15 admissions with CHF within 2 years. Patients with a high N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) and high ROCK activity on admission had a five-fold risk of a cardiovascular event (RR: 5.156; 95% CI: 2.180-12.191) when compared to those with low NT-proBNP and low ROCK activity.
Conclusion: ROCK activity was increased in patients with ACS, particularly in those with myocardial infarction. The combined usage of both ROCK activity and NT-proBNP might identify a subset of ACS patients at particularly high risk.
Keywords: ACS; ANOVA; Acute coronary syndrome; BH; BMI; BW; Body height; Body mass index; Body weight; C-reactive protein; CHD; CHF; CIHD; CPK; CRP; CVA; Cardiac troponin T; Cardio vascular accidents; Congestive heart failure; Coronary heart disease; Coronary ischemic heart disease; Creatine phosphokinase; DBP; DM; Diabetes mellitus; Diastolic blood pressure; Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate; GRACE; Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events; HDL-C; HR; Heart rate; High-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C; LVEF; Left ventricular ejection fraction; Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide; NSTEMI; NT-proBNP; Non-ST elevation myocardial infarction; One-way analysis of variance; PCI; Percutaneous coronary intervention; ROCK; ROCK activity; Rho kinase; Rho kinase activity; SBP; ST elevation myocardial infarction; STEMI; Systolic blood pressure; TC; TG; Total cholesterol; Triglycerides; UA; Unstable angina; WBC; White blood cells; cTnT; eGFR.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Armstrong PW, Fu Y, Chang WC, et al. Acute coronary syndromes in the GUSTO-IIb trial: prognostic insights and impact of recurrent ischemia. Circulation. 1998;98:1860–8. - PubMed
-
- Zaacks SM, Liebson PR, Calvin JE, Parrillo JE, Klein LW. Unstable angina and non-Q wave myocardial infarction: does the clinical diagnosis have therapeutic implications? J Am Coll Cardiol. 1999;33:107–18. - PubMed
-
- Tang EW, Wong CK, Herbison P. Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events (GRACE) hospital discharge risk score accurately predicts long-term mortality post acute coronary syndrome. Am Heart J. 2007;153:29–35. - PubMed
-
- Escudier B, Pluzanska A, Koralewski P, et al. AVOREN Trial investigators. Bevacizumab plus interferon alfa-2a for treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a randomised, double-blind phase III trial. Lancet. 2007;370:2103–11. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

