Enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli exploits a tryptophan switch to hijack host f-actin assembly
- PMID: 22921828
- PMCID: PMC3472031
- DOI: 10.1016/j.str.2012.07.015
Enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli exploits a tryptophan switch to hijack host f-actin assembly
Abstract
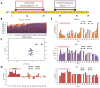
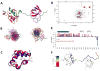
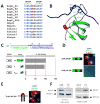
Intrinsically disordered protein (IDP)-mediated interactions are often characterized by low affinity but high specificity. These traits are essential in signaling and regulation that require reversibility. Enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) exploit this situation by commandeering host cytoskeletal signaling to stimulate actin assembly beneath bound bacteria, generating "pedestals" that promote intestinal colonization. EHEC translocates two proteins, EspF(U) and Tir, which form a complex with the host protein IRTKS. The interaction of this complex with N-WASP triggers localized actin polymerization. We show that EspF(U) is an IDP that contains a transiently α-helical N-terminus and dynamic C-terminus. Our structure shows that single EspF(U) repeat forms a high-affinity trimolecular complex with N-WASP and IRTKS. We demonstrate that bacterial and cellular ligands interact with IRTKS SH3 in a similar fashion, but the bacterial protein has evolved to outcompete cellular targets by utilizing a tryptophan switch that offers superior binding affinity enabling EHEC-induced pedestal formation.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Host-pathogen crosstalking: the mastery of taking the helm of the host.Structure. 2012 Oct 10;20(10):1613-5. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2012.09.006. Structure. 2012. PMID: 23063005
References
-
- Babu MM, van der Lee R, de Groot NS, Gsponer J. Intrinsically disordered proteins: regulation and disease. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2011;21:432–440. - PubMed
-
- Campellone KG, Robbins D, Leong JM. EspFU is a translocated EHEC effector that interacts with Tir and N-WASP and promotes Nck-independent actin assembly. Dev Cell. 2004;7:217–228. - PubMed
-
- Campellone KG, Leong JM. Nck-independent actin assembly is mediated by two phosphorylated tyrosines within enteropathogenic Escherichia coli Tir. Mol Microbiol. 2005;56:416–432. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

