Fatty acids as therapeutic auxiliaries for oral and parenteral formulations
- PMID: 22921839
- PMCID: PMC3537895
- DOI: 10.1016/j.addr.2012.07.012
Fatty acids as therapeutic auxiliaries for oral and parenteral formulations
Abstract
Many drugs have decreased therapeutic activity due to issues with absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion. The co-formulation or covalent attachment of drugs with fatty acids has demonstrated some capacity to overcome these issues by improving intestinal permeability, slowing clearance and binding serum proteins for selective tissue uptake and metabolism. For orally administered drugs, albeit at low level of availability, the presence of fatty acids and triglycerides in the intestinal lumen may promote intestinal uptake of small hydrophilic molecules. Small lipophilic drugs or acylated hydrophilic drugs also show increased lymphatic uptake and enhanced passive diffusional uptake. Fatty acid conjugation of small and large proteins or peptides has exhibited protracted plasma half-lives, site-specific delivery and sustained release upon parenteral administration. These improvements are most likely due to associations with lipid-binding serum proteins, namely albumin, LDL and HDL. These molecular interactions, although not fully characterized, could provide the ability of using the endogenous carrier systems for improving therapeutic outcomes.
Keywords: Albumin; Drug absorption; Drug delivery; Drug formulation; Endogenous drug carriers; Fatty acids; Lipid prodrugs; Protein binding; Reversible lipidization; Triglycerides.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures

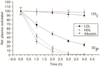
References
-
- Maher S, Leonard TW, Jacobsen J, Brayden DJ. Safety and efficacy of sodium caprate in promoting oral drug absorption: from in vitro to the clinic. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009;61:1427–1449. - PubMed
-
- Lindmark T, Kimura Y, Artursson P. Absorption enhancement through intracellular regulation of tight junction permeability by medium chain fatty acids in Caco-2 cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1998;284:362–369. - PubMed
-
- Soboll S, Gründel S, Schwabe U, Scholz R. Influence of fatty acids on energy metabolism 2 Kinetics of changes in metabolic rates and changes in subcellular adenine nucleotide contents and pH gradients following addition of octanoate and oleate in perfused rat liver. Eur. J. Biochem. 1984;141:231–236. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

