MRI measurements of vessel calibre in tumour xenografts: comparison with vascular corrosion casting
- PMID: 22921880
- PMCID: PMC3657196
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mvr.2012.08.001
MRI measurements of vessel calibre in tumour xenografts: comparison with vascular corrosion casting
Abstract
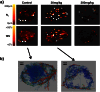
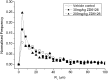
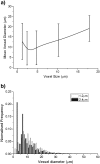
Vessel size index (R(v), μm) has been proposed as a quantitative magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) derived imaging biomarker in oncology, for the non-invasive assessment of tumour blood vessel architecture and vascular targeted therapies. Appropriate pre-clinical evaluation of R(v) in animal tumour models will improve the interpretation and guide the introduction of the biomarker into clinical studies. The objective of this study was to compare R(v) measured in vivo with vessel size measurements from high-resolution X-ray computed tomography (μCT) of vascular corrosion casts measured post mortem from the same tumours, with and without vascular targeted therapy. MRI measurements were first acquired from subcutaneous SW1222 colorectal xenografts in mice following treatment with 0 (n=6), 30 (n=6) or 200 mg/kg (n=3) of the vascular disrupting agent ZD6126. The mice were then immediately infused with a low viscosity resin and, following polymerisation and maceration of surrounding tissues, the resulting tumour vascular casts were dissected and subsequently imaged using an optimised μCT imaging approach. Vessel diameters were not measurable by μCT in the 200 mg/kg group as the high dose of ZD6126 precluded delivery of the resin to the tumour vascular bed. The mean R(v) for the three treatment groups was 24, 23 and 23.5 μm respectively; the corresponding μCT measurements from corrosion casts from the 0 and 30 mg/kg cohorts were 25 and 28 μm. The strong association between the in vivo MRI and post mortem μCT values supports the use of R(v) as an imaging biomarker in clinical trials of investigational vascular targeted therapies.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Abbas B. Radiation induced changes in the blood capillaries of rat duodenal villi: a corrosion cast, light and transmission electron microscopical study. J. Submicrosc. Cytol. Pathol. 1990;22:63–70. - PubMed
-
- Blakey D.C. Antitumor activity of the novel vascular targeting agent ZD6126 in a panel of tumor models. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002;8:1974–1983. - PubMed
-
- Bradley R.S. An examination of phase retrieval algorithms as applied to phase contrast tomography using laboratory sources. In: Stock S.R., editor. Developments in X-ray Tomography VII, San Diego. 2010.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

