Extraocular ectoderm triggers dorsal retinal fate during optic vesicle evagination in zebrafish
- PMID: 22921921
- PMCID: PMC3455121
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.08.004
Extraocular ectoderm triggers dorsal retinal fate during optic vesicle evagination in zebrafish
Abstract
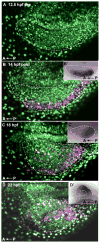
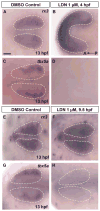
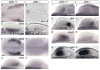
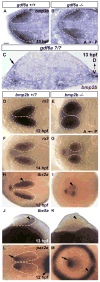
Dorsal retinal fate is established early in eye development, via expression of spatially restricted dorsal-specific transcription factors in the optic vesicle; yet the events leading to initiation of dorsal fate are not clear. We hypothesized that induction of dorsal fate would require an extraocular signal arising from a neighboring tissue to pattern the prospective dorsal retina, however no such signal has been identified. We used the zebrafish embryo to determine the source, timing, and identity of the dorsal retina-inducing signal. Extensive cell movements occur during zebrafish optic vesicle morphogenesis, however the location of prospective dorsal cells within the early optic vesicle and their spatial relationship to early dorsal markers is currently unknown. Our mRNA expression and fate mapping analyses demonstrate that the dorsolateral optic vesicle is the earliest region to express dorsal specific markers, and cells from this domain contribute to the dorsal retinal pole at 24 hpf. We show that three bmp genes marking dorsal retina at 25 hpf are also expressed extraocularly before retinal patterning begins. We identified gdf6a as a dorsal initiation signal acting from the extraocular non-neural ectoderm during optic vesicle evagination. We find that bmp2b is involved in dorsal retina initiation, acting upstream of gdf6a. Together, this work has identified the nature and source of extraocular signals required to pattern the dorsal retina.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Gdf6a is required for the initiation of dorsal-ventral retinal patterning and lens development.Dev Biol. 2009 Sep 1;333(1):37-47. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.06.018. Epub 2009 Jun 21. Dev Biol. 2009. PMID: 19545559
-
Extraocular mesenchyme patterns the optic vesicle during early eye development in the embryonic chick.Development. 2000 Nov;127(21):4599-609. doi: 10.1242/dev.127.21.4599. Development. 2000. PMID: 11023863
-
RPE specification in the chick is mediated by surface ectoderm-derived BMP and Wnt signalling.Development. 2013 Dec;140(24):4959-69. doi: 10.1242/dev.096990. Epub 2013 Nov 13. Development. 2013. PMID: 24227655
-
Eye morphogenesis and patterning of the optic vesicle.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2010;93:61-84. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-385044-7.00003-5. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 20959163 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Eye development and retinogenesis.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2012 Dec 1;4(12):a008391. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a008391. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2012. PMID: 23071378 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Distinct tissue-specific requirements for the zebrafish tbx5 genes during heart, retina and pectoral fin development.Open Biol. 2014 Apr 23;4(4):140014. doi: 10.1098/rsob.140014. Open Biol. 2014. PMID: 24759614 Free PMC article.
-
Abnormal Cone and Rod Photoreceptor Morphogenesis in gdf6a Mutant Zebrafish.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020 Apr 9;61(4):9. doi: 10.1167/iovs.61.4.9. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020. PMID: 32293666 Free PMC article.
-
Morphogenetic defects underlie Superior Coloboma, a newly identified closure disorder of the dorsal eye.PLoS Genet. 2018 Mar 9;14(3):e1007246. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007246. eCollection 2018 Mar. PLoS Genet. 2018. PMID: 29522511 Free PMC article.
-
Antagonism between Gdf6a and retinoic acid pathways controls timing of retinal neurogenesis and growth of the eye in zebrafish.Development. 2016 Apr 1;143(7):1087-98. doi: 10.1242/dev.130922. Epub 2016 Feb 18. Development. 2016. PMID: 26893342 Free PMC article.
-
Dorsoventral patterning of the Xenopus eye involves differential temporal changes in the response of optic stalk and retinal progenitors to Hh signalling.Neural Dev. 2015 Mar 20;10:7. doi: 10.1186/s13064-015-0035-9. Neural Dev. 2015. PMID: 25886149 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asai-Coakwell M, French CR, Ye M, Garcha K, Bigot K, Perera AG, Staehling-Hampton K, Mema SC, Chanda B, Mushegian A, Bamforth S, Doschak MR, Li G, Dobbs MB, Giampietro PF, Brooks BP, Vijayalakshmi P, Sauve Y, Abitbol M, Sundaresan P, van Heyningen V, Pourquie O, Underhill TM, Waskiewicz AJ, Lehmann OJ. Incomplete penetrance and phenotypic variability characterize Gdf6-attributable oculo-skeletal phenotypes. Hum Mol Genet. 2009;18:1110–21. - PubMed
-
- Dheen T, Sleptsova-Friedrich I, Xu Y, Clark M, Lehrach H, Gong Z, Korzh V. Zebrafish tbx-c functions during formation of midline structures. Development. 1999;126:2703–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

