Two functional domains in C. elegans glypican LON-2 can independently inhibit BMP-like signaling
- PMID: 22922164
- PMCID: PMC5705046
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.08.006
Two functional domains in C. elegans glypican LON-2 can independently inhibit BMP-like signaling
Abstract
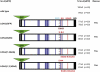
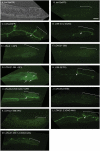
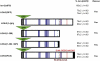
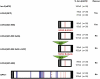
Glypicans are multifunctional proteoglycans with regulatory roles in several intercellular signaling pathways. Here, we examine the functional requirements for glypican regulation of bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-mediated body length in C. elegans. We provide evidence that two parts of C. elegans glypican LON-2 can independently inhibit BMP signaling in vivo: the N-terminal furin protease product and the C-terminal region containing heparan sulfate attachment sequences. While the C-terminal protease product is dispensable for LON-2 minimal core protein activity, it does affect the localization of LON-2. Cleavage of LON-2 into two parts at the conserved furin protease site is not required for LON-2 to inhibit BMP-like signaling. The glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol (GPI) membrane anchor is also not absolutely required for LON-2 activity. Finally, we show that an RGD protein-protein interaction motif in the LON-2 N-terminal domain is necessary for LON-2 core protein activity, suggesting that LON-2 inhibits BMP signaling by acting as a scaffold for BMP and an RGD-binding protein.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Regulation of TGFβ superfamily signaling by two separable domains of glypican LON-2 in C. elegans.Worm. 2013 Jul 1;2(3):e23843. doi: 10.4161/worm.23843. Epub 2013 Oct 1. Worm. 2013. PMID: 24778932 Free PMC article.
-
Glypican LON-2 is a conserved negative regulator of BMP-like signaling in Caenorhabditis elegans.Curr Biol. 2007 Jan 23;17(2):159-64. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2006.11.065. Curr Biol. 2007. PMID: 17240342
-
SMOC-1 interacts with both BMP and glypican to regulate BMP signaling in C. elegans.PLoS Biol. 2023 Aug 17;21(8):e3002272. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002272. eCollection 2023 Aug. PLoS Biol. 2023. PMID: 37590248 Free PMC article.
-
Glypicans.Genome Biol. 2008;9(5):224. doi: 10.1186/gb-2008-9-5-224. Epub 2008 May 22. Genome Biol. 2008. PMID: 18505598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of glypican-1 in regulating multiple cellular signaling pathways.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2021 Nov 1;321(5):C846-C858. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00290.2021. Epub 2021 Sep 22. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34550795 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of extracellular matrix organization by BMP signaling in Caenorhabditis elegans.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 11;9(7):e101929. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101929. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25013968 Free PMC article.
-
Agonists and Antagonists of TGF-β Family Ligands.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2016 Aug 1;8(8):a021923. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a021923. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2016. PMID: 27413100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AP2M1 Supports TGF-β Signals to Promote Collagen Expression by Inhibiting Caveolin Expression.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 6;22(4):1639. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041639. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33561975 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of TGFβ superfamily signaling by two separable domains of glypican LON-2 in C. elegans.Worm. 2013 Jul 1;2(3):e23843. doi: 10.4161/worm.23843. Epub 2013 Oct 1. Worm. 2013. PMID: 24778932 Free PMC article.
-
Repulsive guidance molecules (RGMs) and neogenin in bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling.Mol Reprod Dev. 2013 Sep;80(9):700-17. doi: 10.1002/mrd.22199. Epub 2013 Jul 19. Mol Reprod Dev. 2013. PMID: 23740870 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baeg GH, Lin X, Khare N, Baumgartner S, Perrimon N. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans are critical for the organization of the extracellular distribution of Wingless. Development. 2001;128:87–94. - PubMed
-
- Bernfield M, Gotte M, Park PW, Reizes O, Fitzgerald ML, Lincecum J, Zako M. Functions of cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1999;68:729–777. - PubMed
-
- Brandan E, Carey DJ, Larrain J, Melo F, Campos A. Synthesis and processing of glypican during differentiation of skeletal muscle cells. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 1996;71:170–176. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

