Engineering influenza viral vectors
- PMID: 22922205
- PMCID: PMC3566024
- DOI: 10.4161/bioe.21950
Engineering influenza viral vectors
Abstract
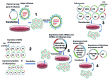
The influenza virus is a respiratory pathogen with a negative-sense, segmented RNA genome. Construction of recombinant influenza viruses in the laboratory was reported starting in the 1980s. Within a short period of time, pioneer researchers had devised methods that made it possible to construct influenza viral vectors from cDNA plasmid systems. Herein, we discuss the evolution of influenza virus reverse genetics, from helper virus-dependent systems, to helper virus-independent 17-plasmid systems, and all the way to 3- and 1- plasmid systems. Successes in the modification of different gene segments for various applications, including vaccine and gene therapies are highlighted.
Keywords: gene delivery; gene therapy; influenza virus; microRNA delivery; pseudo-typed virus; reverse genetics; vaccine; viral vector.
Figures
References
-
- Avilov SV, Moisy D, Munier S, Schraidt O, Naffakh N, Cusack S. Replication-competent influenza A virus that encodes a split-green fluorescent protein-tagged PB2 polymerase subunit allows live-cell imaging of the virus life cycle. J Virol. 2012;86:1433–48. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05820-11. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
