Formononetin attenuates IL-1β-induced apoptosis and NF-κB activation in INS-1 cells
- PMID: 22922276
- PMCID: PMC6268495
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules170910052
Formononetin attenuates IL-1β-induced apoptosis and NF-κB activation in INS-1 cells
Abstract
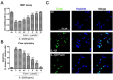
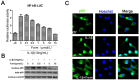
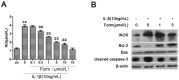
Several studies suggest that the inflammation plays a role in the pathogenesis of some glucose disorders in adults. Exposure of pancreatic β-cells to cytokines, such as interleukin-1β (IL-1β), is thought to contribute to β-cell apoptosis. One important event triggered by IL-1β is induction of nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), an enzyme that catalyzes intracellular generation of the cytotoxic free radical NO. Recent work have suggested that formononetin, as an O-methylated isoflavone found in a number of plants and herbs like Astragalus membranaceus, inhibited some pro-inflammatory cytokine production in macrophages. However, the roles of formononetin in pancreatic beta cells have not been fully established. The aim of the present study was to assess possible in vitro effects of formononetin on cell apoptosis induced by IL-1β in the rat insulinoma cell line, INS-1. Our results demonstrate that formononetin significantly prevents IL-1β-increased INS-1 cell death and blocks cytokine-induced apoptotic signaling (the reduction of Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and caspase-3 activity). Formononetin also inhibited the activation of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB), which is a significant transcription factor for iNOS, so as to decease nitric oxide (NO) formation in a dose dependent manner in vitro. Our observations indicated that formononetin could protect against pancreatic β-cell apoptosis caused by IL-1β and therefore could be used in the future as a new drug improving diabetes mellitus.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Induction of nuclear factor-kappaB and its downstream genes by TNF-alpha and IL-1beta has a pro-apoptotic role in pancreatic beta cells.Diabetologia. 2008 Jul;51(7):1213-25. doi: 10.1007/s00125-008-0999-7. Epub 2008 May 8. Diabetologia. 2008. PMID: 18463842
-
Exendin-4 protects murine MIN6 pancreatic β-cells from interleukin-1β-induced apoptosis via the NF-κB pathway.J Endocrinol Invest. 2013 Nov;36(10):803-11. doi: 10.3275/8938. Epub 2013 Apr 18. J Endocrinol Invest. 2013. PMID: 23609920
-
Cytokine-induced proapoptotic gene expression in insulin-producing cells is related to rapid, sustained, and nonoscillatory nuclear factor-kappaB activation.Mol Endocrinol. 2006 Aug;20(8):1867-79. doi: 10.1210/me.2005-0268. Epub 2006 Mar 23. Mol Endocrinol. 2006. PMID: 16556731
-
Neuroprotective potential of formononetin, a naturally occurring isoflavone phytoestrogen.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2024 Jan;103(1):e14353. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.14353. Epub 2023 Sep 18. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2024. PMID: 37722967 Review.
-
Flavonoids, Isoflavonoids and others Bioactives for Insulin Sensitizations.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2024;20(2):e270423216247. doi: 10.2174/1573399819666230427095200. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2024. PMID: 37102490 Review.
Cited by
-
The non-canonical NF-κB pathway is induced by cytokines in pancreatic beta cells and contributes to cell death and proinflammatory responses in vitro.Diabetologia. 2016 Mar;59(3):512-21. doi: 10.1007/s00125-015-3817-z. Epub 2015 Dec 3. Diabetologia. 2016. PMID: 26634571
-
Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Formononetin 7-O-phosphate, a Novel Biorenovation Product, on LPS-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Macrophage Cells.Molecules. 2019 Oct 30;24(21):3910. doi: 10.3390/molecules24213910. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31671623 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Isoflavones in Type 2 Diabetes Prevention and Treatment-A Narrative Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 28;22(1):218. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010218. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33379327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Propolis Stands out as a Multifaceted Natural Product: Meta-Analysis on Its Sources, Bioactivities, Applications, and Future Perspectives.Life (Basel). 2025 May 9;15(5):764. doi: 10.3390/life15050764. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40430191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modeling long-term host cell-Giardia lamblia interactions in an in vitro co-culture system.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 3;8(12):e81104. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081104. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24312526 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bowie A., O’Neill L.A. The interleukin-1 receptor/Toll-like receptor superfamily: Signal generators for pro-inflammatory interleukins and microbial products. J. Leuk. Biol. 2000;67:508–514. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

