Emodin, an 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 inhibitor, regulates adipocyte function in vitro and exerts anti-diabetic effect in ob/ob mice
- PMID: 22922341
- PMCID: PMC4003114
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2012.87
Emodin, an 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 inhibitor, regulates adipocyte function in vitro and exerts anti-diabetic effect in ob/ob mice
Abstract
Aim: Emodin (1,3,8-trihydroxy-6-methylanthraquinone) is a potent and selective inhibitor of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 (11β-HSD1) with the ability to ameliorate metabolic disorders in diet-induced obese mice. In the present study, we investigated the effects of emodin on adipocyte function and the underlying mechanisms in vitro, and its anti-diabetic effects in ob/ob mice.
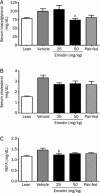
Methods: 3T3-L1 adipocytes were used for in vitro studies. 11β-HSD1A activity was evaluated with a scintillation proximity assay. The adipogenesis, glucose uptake, lipolysis and adiponectin secretion were investigated in 3T3-L1 adipocytes treated with emodin in the presence of active (corticosterone) or inactive glucocorticoid (11-dehydrocorticosterone). For in vivo studies, ob/ob mice were administered emodin (25 and 50 mg·kg⁻¹·d⁻¹, ip) for 26 d. On the last day of administration, the serum was collected and the mesenteric and perirenal fat were dissected for analyses.
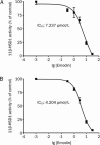
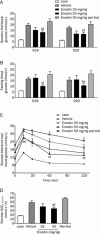
Results: Emodin inhibited the 11β-HSD1 activity in 3T3-L1 adipocytes in concentration- and time-dependent manners (the IC₅₀ values were 7.237 and 4.204 μmol/L, respectively, after 1 and 24 h treatment. In 3T3-L1 adipocytes, emodin (30 μmol/L) suppressed 11-dehydrocorticosterone-induced adipogenesis without affecting corticosterone-induced adipogenesis; emodin (3 μmol/L) reduced 11-dehydrocorticosterone-stimulated lipolysis, but had no effect on corticosterone-induced lipolysis. Moreover, emodin (3 μmol/L) partly reversed the impaired insulin-stimulated glucose uptake and adiponectin secretion induced by 11-dehydrocorticosterone but not those induced by corticosterone. In ob/ob mice, long-term emodin administration decreased 11β-HSD1 activity in mesenteric adipose tissues, lowered non-fasting and fasting blood glucose levels, and improved glucose tolerance.
Conclusion: Emodin improves the inactive glucocorticoid-induced adipose tissue dysfunction by selective inhibition on 11β-HSD1 in adipocyte in vitro and improves glycemic control in ob/ob mice.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Anti-diabetic and anti-adipogenic effects of a novel selective 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 inhibitor in the diet-induced obese mice.Eur J Pharmacol. 2012 Sep 15;691(1-3):19-27. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2012.06.024. Epub 2012 Jul 1. Eur J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22760069
-
Anti-diabetic and anti-adipogenic effects of a novel selective 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 inhibitor, 2-(3-benzoyl)-4-hydroxy-1,1-dioxo-2H-1,2-benzothiazine-2-yl-1-phenylethanone (KR-66344).Biochem Pharmacol. 2011 Apr 15;81(8):1028-35. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2011.01.020. Epub 2011 Feb 18. Biochem Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21315688
-
Anti-diabetic and anti-inflammatory effect of a novel selective 11β-HSD1 inhibitor in the diet-induced obese mice.Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Dec 5;721(1-3):70-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.09.052. Epub 2013 Oct 14. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24135201
-
Tissue-specific glucocorticoid reactivating enzyme, 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 (11 beta-HSD1)--a promising drug target for the treatment of metabolic syndrome.Curr Drug Targets Immune Endocr Metabol Disord. 2003 Dec;3(4):255-62. doi: 10.2174/1568008033340135. Curr Drug Targets Immune Endocr Metabol Disord. 2003. PMID: 14683456 Review.
-
11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 and obesity.Front Horm Res. 2008;36:146-164. doi: 10.1159/000115363. Front Horm Res. 2008. PMID: 18230901 Review.
Cited by
-
Celebrating the 80th anniversary of the Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences (SIMM).Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012 Sep;33(9):1101-2. doi: 10.1038/aps.2012.131. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012. PMID: 22948617 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Tissue-specific dysregulation of cortisol regeneration by 11βHSD1 in obesity: has it promised too much?Diabetologia. 2014 Jun;57(6):1100-10. doi: 10.1007/s00125-014-3228-6. Epub 2014 Apr 8. Diabetologia. 2014. PMID: 24710966 Review.
-
Advances in the pharmacological effects and molecular mechanisms of emodin in the treatment of metabolic diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Oct 31;14:1240820. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1240820. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 38027005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of Emodin as a Therapeutic Agent for Diabetic Cataract.J Nat Prod. 2016 May 27;79(5):1439-44. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.6b00185. Epub 2016 May 3. J Nat Prod. 2016. PMID: 27140653 Free PMC article.
-
New opportunities and challenges of natural products research: When target identification meets single-cell multiomics.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022 Nov;12(11):4011-4039. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2022.08.022. Epub 2022 Aug 27. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022. PMID: 36386472 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Beauregard C, Dickstein G, Lacroix A. Classic and recent etiologies of Cushing's syndrome: diagnosis and therapy. Treat Endocrinol. 2002;1:79–94. - PubMed
-
- Seckl JR, Walker BR. Minireview: 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1- a tissue-specific amplifier of glucocorticoid action. Endocrinology. 2001;142:1371–6. - PubMed
-
- Morton NM. Obesity and corticosteroids: 11beta–hydroxysteroid type 1 as a cause and therapeutic target in metabolic disease. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010;316:154–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

