CDKL5 ensures excitatory synapse stability by reinforcing NGL-1-PSD95 interaction in the postsynaptic compartment and is impaired in patient iPSC-derived neurons
- PMID: 22922712
- PMCID: PMC6485419
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566
CDKL5 ensures excitatory synapse stability by reinforcing NGL-1-PSD95 interaction in the postsynaptic compartment and is impaired in patient iPSC-derived neurons
Abstract
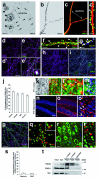
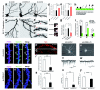
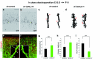
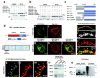
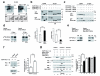
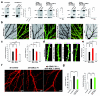
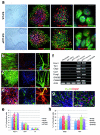
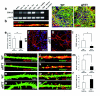
Mutations of the cyclin-dependent kinase-like 5 (CDKL5) and netrin-G1 (NTNG1) genes cause a severe neurodevelopmental disorder with clinical features that are closely related to Rett syndrome, including intellectual disability, early-onset intractable epilepsy and autism. We report here that CDKL5 is localized at excitatory synapses and contributes to correct dendritic spine structure and synapse activity. To exert this role, CDKL5 binds and phosphorylates the cell adhesion molecule NGL-1. This phosphorylation event ensures a stable association between NGL-1 and PSD95. Accordingly, phospho-mutant NGL-1 is unable to induce synaptic contacts whereas its phospho-mimetic form binds PSD95 more efficiently and partially rescues the CDKL5-specific spine defects. Interestingly, similarly to rodent neurons, iPSC-derived neurons from patients with CDKL5 mutations exhibit aberrant dendritic spines, thus suggesting a common function of CDKL5 in mice and humans.
Figures
References
-
- Bienvenu T, Chelly J. Molecular genetics of Rett syndrome: when DNA methylation goes unrecognized. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006;7:415–426. - PubMed
-
- Chahrour M, Zoghbi HY. The story of Rett syndrome: from clinic to neurobiology. Neuron. 2007;56:422–437. - PubMed
-
- Amir RE, Van den Veyver IB, Wan M, Tran CQ, Francke U, Zoghbi HY. Rett syndrome is caused by mutations in X-linked MECP2, encoding methyl-CpG-binding protein 2. Nat. Genet. 1999;23:185–188. - PubMed
-
- Francke U. Mechanisms of disease: neurogenetics of MeCP2 deficiency. Nat. Clin. Pract. Neurol. 2006;2:212–221. - PubMed
-
- Tao J, Van Esch H, Hagedorn-Greiwe M, Hoffmann K, Moser B, Raynaud M, Sperner J, Fryns JP, Schwinger E, Gécz J, et al. Mutations in the X-linked cyclin-dependent kinase-like 5 (CDKL5/STK9) gene are associated with severe neurodevelopmental retardation. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2004;75:1149–1154. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

