Pyruvate kinase M2 activators promote tetramer formation and suppress tumorigenesis
- PMID: 22922757
- PMCID: PMC3711671
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.1060
Pyruvate kinase M2 activators promote tetramer formation and suppress tumorigenesis
Erratum in
- Nat Chem Biol. 2012 Dec;8(12):1008
Abstract
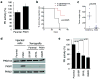
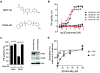
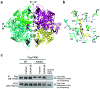
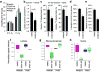
Cancer cells engage in a metabolic program to enhance biosynthesis and support cell proliferation. The regulatory properties of pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2) influence altered glucose metabolism in cancer. The interaction of PKM2 with phosphotyrosine-containing proteins inhibits enzyme activity and increases the availability of glycolytic metabolites to support cell proliferation. This suggests that high pyruvate kinase activity may suppress tumor growth. We show that expression of PKM1, the pyruvate kinase isoform with high constitutive activity, or exposure to published small-molecule PKM2 activators inhibits the growth of xenograft tumors. Structural studies reveal that small-molecule activators bind PKM2 at the subunit interaction interface, a site that is distinct from that of the endogenous activator fructose-1,6-bisphosphate (FBP). However, unlike FBP, binding of activators to PKM2 promotes a constitutively active enzyme state that is resistant to inhibition by tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins. These data support the notion that small-molecule activation of PKM2 can interfere with anabolic metabolism.
Conflict of interest statement
L.C.C. is a founder, M.V.H. is a consultant, and A.J., H.Y., C.K., K.E.Y., K.K., F.G.S., S.J. L.D are employed by Agios Pharmaceuticals, a company seeking to target metabolic enzymes for cancer therapy.
Figures


References
-
- Tennant DA, Duran RV, Gottlieb E. Targeting metabolic transformation for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10:267–77. - PubMed
-
- Vander Heiden MG. Targeting cancer metabolism: a therapeutic window opens. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011;10:671–84. - PubMed
-
- Cairns RA, Harris IS, Mak TW. Regulation of cancer cell metabolism. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;11:85–95. - PubMed
-
- Levine AJ, Puzio-Kuter AM. The control of the metabolic switch in cancers by oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes. Science. 2010;330:1340–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- 5P30CA006516/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- P01 CA120964/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 CA160458/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM56203/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 5P30CA1405141/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA006516/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5P01CA120964/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R03MH085679/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R03 MH085679/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM056203/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

