Engineered domain-based assays to identify individual antibodies in oligoclonal combinations targeting the same protein
- PMID: 22922799
- PMCID: PMC4209713
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ab.2012.08.005
Engineered domain-based assays to identify individual antibodies in oligoclonal combinations targeting the same protein
Abstract
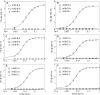
Quantitation of individual monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) within a combined antibody drug product is required for preclinical and clinical drug development. We have developed two antitoxins, XOMA 3B and XOMA 3E, each consisting of three mAbs that neutralize type B and type E botulinum neurotoxin (BoNT/B and BoNT/E) to treat serotype B and E botulism. To develop mAb-specific binding assays for each antitoxin, we mapped the epitopes of the six mAbs. Each mAb bound an epitope on either the BoNT light chain (LC) or translocation domain (H(N)). Epitope mapping data were used to design LC-H(N) domains with orthogonal mutations to make them specific for only one mAb in either XOMA 3B or XOMA 3E. Mutant LC-H(N) domains were cloned, expressed, and purified from Escherichia coli. Each mAb bound only to its specific domain with affinity comparable to the binding to holotoxin. Further engineering of domains allowed construction of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) that could characterize the integrity, binding affinity, and identity of each of the six mAbs in XOMA 3B and 3E without interference from the three BoNT/A mAbs in XOMA 3AB. Such antigen engineering is a general method allowing quantitation and characterization of individual mAbs in a mAb cocktail that bind the same protein.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
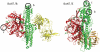



References
-
- Nelson AL, Dhimolea E, Reichert JM. Development trends for human monoclonal antibody therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010;9:767–774. - PubMed
-
- Logtenberg T. Antibody cocktails: next-generation biopharmaceuticals with improved potency. Trends Biotechnol. 2007;25:390–394. - PubMed
-
- Bakker AB, Python C, Kissling CJ, Pandya P, Marissen WE, Brink MF, Lagerwerf F, Worst S, van Corven E, Kostense S, Hartmann K, Weverling GJ, Uytdehaag F, Herzog C, Briggs DJ, Rupprecht CE, Grimaldi R, Goudsmit J. First administration to humans of a monoclonal antibody cocktail against rabies virus: safety, tolerability, and neutralizing activity. Vaccine. 2008;26:5922–5927. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

