Inducible IL-33 expression by mast cells is regulated by a calcium-dependent pathway
- PMID: 22922818
- PMCID: PMC3541686
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1201224
Inducible IL-33 expression by mast cells is regulated by a calcium-dependent pathway
Abstract
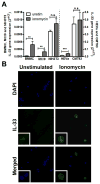
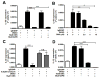
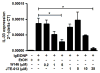
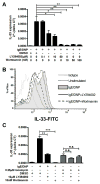
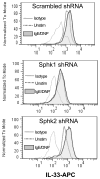
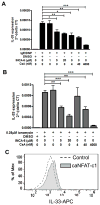
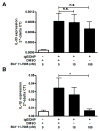
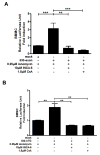
IL-33 is an IL-1 family cytokine that displays dual functions: a cytokine via its receptor, T1/ST2, or a chromatin-binding factor within the nucleus. Functionally, it promotes Th2-associated immunity by enhancing the activation and survival of several cell types. However, the pathways regulating IL-33 expression are still unclear. Although several cells display constitutive expression of IL-33, we showed previously that mast cells expressed low levels of IL-33 constitutively but that IL-33 was induced upon IgE-mediated activation. This was mediated via a calcium-dependent mechanism. In this study, we define the pathway through which this inducible IL-33 is regulated. Importantly, this pathway does not alter expression in cells with high constitutive IL-33 expression, such as epithelial cells or fibroblasts. Our data show that, upstream of calcium, inhibition of PI3K and Sphk activity decreases inducible IL-33 expression to IgE/Ag activation. Additionally, expression of Sphk1 short hairpin RNA prevents upregulation of IL-33 expression. Downstream of calcium, NFAT activity is necessary and sufficient for inducible IL-33 expression. We also demonstrate calcium-dependent transcription from two regions of the IL-33 gene that contain putative NFAT-binding sites, one upstream of exon 1 and one upstream of the start site. Interestingly, we show that blocking other calcium pathways, including inositol triphosphate receptor, or NF-κB inhibits IgE-driven IL-1β, another IL-1 family cytokine, but it has no influence on inducible IL-33 expression. In summary, our data demonstrate cell-specific differences in the regulation of IL-33 expression and define a pathway critical for the expression of inducible IL-33 by mast cells upon their activation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
IL-33 is produced by mast cells and regulates IgE-dependent inflammation.PLoS One. 2010 Aug 3;5(8):e11944. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011944. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20689814 Free PMC article.
-
Fc epsilon RI-mediated induction of nuclear factor of activated T-cells.J Biol Chem. 1995 Jul 7;270(27):16333-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.27.16333. J Biol Chem. 1995. PMID: 7608202
-
Transcriptional activation of the IL31 gene by NFAT and STAT6.J Leukoc Biol. 2012 Feb;91(2):245-57. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0111020. Epub 2011 Nov 1. J Leukoc Biol. 2012. PMID: 22045870
-
NFAT but not NF-kappaB is critical for transcriptional induction of the prosurvival gene A1 after IgE receptor activation in mast cells.Blood. 2008 Mar 15;111(6):3081-9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-10-053371. Epub 2008 Jan 8. Blood. 2008. PMID: 18182578 Free PMC article.
-
Role of activator protein 1, nuclear factor-kappaB, and nuclear factor of activated T cells in IgE receptor-mediated cytokine expression in mature human mast cells.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003 May;111(5):1062-8. doi: 10.1067/mai.2003.1342. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12743571
Cited by
-
Allergic inflammation is initiated by IL-33-dependent crosstalk between mast cells and basophils.PLoS One. 2020 Jan 15;15(1):e0226701. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0226701. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 31940364 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional Heterogeneity of Mast Cells and Basophils upon Activation.J Immunol. 2017 Jun 15;198(12):4868-4878. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1601825. Epub 2017 May 5. J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28476932 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Sphingosine-1-Phosphate in Mast Cell Functions and Asthma and Its Regulation by Non-Coding RNA.Front Immunol. 2017 May 22;8:587. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00587. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28588581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Crosstalk between FcεRI and Sphingosine Signaling in Allergic Inflammation.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 11;23(22):13892. doi: 10.3390/ijms232213892. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430378 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory Mechanism of the IL-33-IL-37 Axis via Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor in Atopic Dermatitis and Psoriasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 27;24(19):14633. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914633. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834081 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schmitz J, Owyang A, Oldham E, Song Y, Murphy E, McClanahan TK, Zurawski G, Moshrefi M, Qin J, Li X, Gorman DM, Bazan JF, Kastelein RA. IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1 receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated cytokines. Immunity. 2005;23:479–90. - PubMed
-
- Chackerian AA, Oldham ER, Murphy EE, Schmitz J, Pflanz S, Kastelein RA. IL-1 receptor accessory protein and ST2 comprise the IL-33 receptor complex. J Immunol. 2007;179:2551–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

