Flow control in our vessels: vascular valves make sure there is no way back
- PMID: 22922986
- PMCID: PMC3578722
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-012-1110-6
Flow control in our vessels: vascular valves make sure there is no way back
Abstract
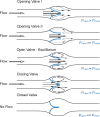
The efficient transport of blood and lymph relies on competent intraluminal valves that ensure unidirectional fluid flow through the vessels. In the lymphatic vessels, lack of luminal valves causes reflux of lymph and can lead to lymphedema, while dysfunction of venous valves is associated with venous hypertension, varicose veins, and thrombosis that can lead to edema and ulcerations. Despite their clinical importance, the mechanisms that regulate valve formation are poorly understood and have only recently begun to be characterized. Here, we discuss new findings regarding the development of venous and lymphatic valves that indicate the involvement of common molecular mechanisms in regulating valve formation in different vascular beds.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

