Gain-of-function mutations in UPC2 are a frequent cause of ERG11 upregulation in azole-resistant clinical isolates of Candida albicans
- PMID: 22923048
- PMCID: PMC3485914
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.00215-12
Gain-of-function mutations in UPC2 are a frequent cause of ERG11 upregulation in azole-resistant clinical isolates of Candida albicans
Abstract
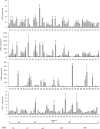
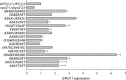
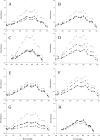
In Candida albicans, Upc2 is a zinc-cluster transcription factor that targets genes, including those of the ergosterol biosynthesis pathway. To date, three documented UPC2 gain-of-function (GOF) mutations have been recovered from fluconazole-resistant clinical isolates that contribute to an increase in ERG11 expression and decreased fluconazole susceptibility. In a group of 63 isolates with reduced susceptibility to fluconazole, we found that 47 overexpressed ERG11 by at least 2-fold over the average expression levels in 3 unrelated fluconazole-susceptible strains. Of those 47 isolates, 29 contained a mutation in UPC2, whereas the remaining 18 isolates did not. Among the isolates containing mutations in UPC2, we recovered eight distinct mutations resulting in putative single amino acid substitutions: G648D, G648S, A643T, A643V, Y642F, G304R, A646V, and W478C. Seven of these resulted in increased ERG11 expression, increased cellular ergosterol, and decreased susceptibility to fluconazole compared to the results for the wild-type strain. Genome-wide transcriptional analysis was performed for the four strongest Upc2 amino acid substitutions (A643V, G648D, G648S, and Y642F). Genes commonly upregulated by all four mutations included those involved in ergosterol biosynthesis, in oxidoreductase activity, the major facilitator efflux pump encoded by the MDR1 gene, and the uncharacterized ATP binding cassette transporter CDR11. These findings demonstrate that gain-of-function mutations in UPC2 are more prevalent among clinical isolates than previously thought and make a significant contribution to azole antifungal resistance, but the findings do not account for ERG11 overexpression in all such isolates of C. albicans.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An A643T mutation in the transcription factor Upc2p causes constitutive ERG11 upregulation and increased fluconazole resistance in Candida albicans.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010 Jan;54(1):353-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01102-09. Epub 2009 Nov 2. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010. PMID: 19884367 Free PMC article.
-
A gain-of-function mutation in the transcription factor Upc2p causes upregulation of ergosterol biosynthesis genes and increased fluconazole resistance in a clinical Candida albicans isolate.Eukaryot Cell. 2008 Jul;7(7):1180-90. doi: 10.1128/EC.00103-08. Epub 2008 May 16. Eukaryot Cell. 2008. PMID: 18487346 Free PMC article.
-
MDR1 overexpression combined with ERG11 mutations induce high-level fluconazole resistance in Candida tropicalis clinical isolates.BMC Infect Dis. 2018 Apr 10;18(1):162. doi: 10.1186/s12879-018-3082-0. BMC Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 29631565 Free PMC article.
-
Screening for amino acid substitutions in the Candida albicans Erg11 protein of azole-susceptible and azole-resistant clinical isolates: new substitutions and a review of the literature.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2010 Apr;66(4):373-84. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2009.11.006. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2010. PMID: 20226328 Review.
-
Molecular epidemiology, antifungal susceptibility, and ERG11 gene mutation of Candida species isolated from vulvovaginal candidiasis: Comparison between recurrent and non-recurrent infections.Microb Pathog. 2022 Sep;170:105696. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105696. Epub 2022 Jul 31. Microb Pathog. 2022. PMID: 35921954 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibitory effect of magnetic iron-oxide nanoparticles on the pattern of expression of lanosterol 14α-demethylase (ERG11) in fluconazole-resistant colonising isolate of Candida albicans.IET Nanobiotechnol. 2020 Jul;14(5):375-381. doi: 10.1049/iet-nbt.2019.0354. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32691739 Free PMC article.
-
Manganese homeostasis modulates fungal virulence and stress tolerance in Candida albicans.mSphere. 2024 Mar 26;9(3):e0080423. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00804-23. Epub 2024 Feb 21. mSphere. 2024. PMID: 38380913 Free PMC article.
-
Mathematical Modeling of Fluconazole Resistance in the Ergosterol Pathway of Candida albicans.mSystems. 2022 Dec 20;7(6):e0069122. doi: 10.1128/msystems.00691-22. Epub 2022 Nov 16. mSystems. 2022. PMID: 36383015 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Characterization of a Biaryl Amide Anti-virulence Compound Targeting Candida albicans Filamentation and Biofilm Formation.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018 Jul 10;8:227. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00227. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30042929 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of Upc2p-Inducible ERG3 Transcription Is Sufficient To Confer Niche-Specific Azole Resistance without Compromising Candida albicans Pathogenicity.mBio. 2018 May 22;9(3):e00225-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00225-18. mBio. 2018. PMID: 29789366 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute 2008. Reference method for broth dilution antifungal susceptibility testing of yeasts; approved method M27-A3. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne, PA
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

