The doublesex homolog Dmrt5 is required for the development of the caudomedial cerebral cortex in mammals
- PMID: 22923088
- PMCID: PMC3792737
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhs234
The doublesex homolog Dmrt5 is required for the development of the caudomedial cerebral cortex in mammals
Abstract
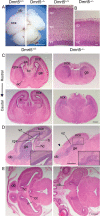
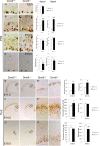
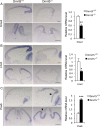
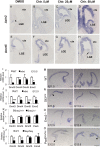
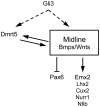
Regional patterning of the cerebral cortex is initiated by morphogens secreted by patterning centers that establish graded expression of transcription factors within cortical progenitors. Here, we show that Dmrt5 is expressed in cortical progenitors in a high-caudomedial to low-rostrolateral gradient. In its absence, the cortex is strongly reduced and exhibits severe abnormalities, including agenesis of the hippocampus and choroid plexus and defects in commissural and thalamocortical tracts. Loss of Dmrt5 results in decreased Wnt and Bmp in one of the major telencephalic patterning centers, the dorsomedial telencephalon, and in a reduction of Cajal-Retzius cells. Expression of the dorsal midline signaling center-dependent transcription factors is downregulated, including Emx2, which promotes caudomedial fates, while the rostral determinant Pax6, which is inhibited by midline signals, is upregulated. Consistently, Dmrt5(-/-) brains exhibit patterning defects with a dramatic reduction of the caudomedial cortex. Dmrt5 is increased upon the activation of Wnt signaling and downregulated in Gli3(xt/xt) mutants. We conclude that Dmrt5 is a novel Wnt-dependent transcription factor required for early cortical development and that it may regulate initial cortical patterning by promoting dorsal midline signaling center formation and thereby helping to establish the graded expression of the other transcription regulators of cortical identity.
Keywords: Emx2; Wnt/Bmp; choroid plexus; cortical hem; telencephalon.
Figures




References
-
- Allendoerfer KL, Shatz CJ. The subplate, a transient neocortical structure: Its role in the development of connections between thalamus and cortex. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1994;17:185–218. - PubMed
-
- Aoto K, Nishimura T, Eto K, Motoyama J. Mouse GLI3 regulates Fgf8 expression and apoptosis in the developing neural tube, face, and limb bud. Dev Biol. 2002;251:320–332. - PubMed
-
- Armentano M, Chou SJ, Tomassy GS, Leingärtner A, O'Leary DD, Studer M. COUP-TF1 regulates the balance of cortical patterning between frontal/motor and sensory areas. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10:1277–1286. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

