Improved predictions of transcription factor binding sites using physicochemical features of DNA
- PMID: 22923524
- PMCID: PMC3526315
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gks771
Improved predictions of transcription factor binding sites using physicochemical features of DNA
Abstract
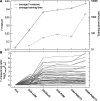
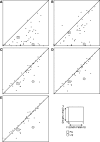
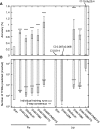
Typical approaches for predicting transcription factor binding sites (TFBSs) involve use of a position-specific weight matrix (PWM) to statistically characterize the sequences of the known sites. Recently, an alternative physicochemical approach, called SiteSleuth, was proposed. In this approach, a linear support vector machine (SVM) classifier is trained to distinguish TFBSs from background sequences based on local chemical and structural features of DNA. SiteSleuth appears to generally perform better than PWM-based methods. Here, we improve the SiteSleuth approach by considering both new physicochemical features and algorithmic modifications. New features are derived from Gibbs energies of amino acid-DNA interactions and hydroxyl radical cleavage profiles of DNA. Algorithmic modifications consist of inclusion of a feature selection step, use of a nonlinear kernel in the SVM classifier, and use of a consensus-based post-processing step for predictions. We also considered SVM classification based on letter features alone to distinguish performance gains from use of SVM-based models versus use of physicochemical features. The accuracy of each of the variant methods considered was assessed by cross validation using data available in the RegulonDB database for 54 Escherichia coli TFs, as well as by experimental validation using published ChIP-chip data available for Fis and Lrp.
Figures

References
-
- Holtz WJ, Keasling JD. Engineering static and dynamic control of synthetic pathways. Cell. 2010;140:19–23. - PubMed
-
- Johnson DS, Mortazavi A, Myers RM, Wold B. Genome-wide mapping of in vivo protein-DNA interactions. Science. 2007;316:1497–1502. - PubMed
-
- Robertson G, Hirst M, Bainbridge M, Bilenky M, Zhao Y, Zeng T, Euskirchen G, Bernier B, Varhol R, Delaney A, et al. Genome-wide profiles of STAT1 DNA association using chromatin immunoprecipitation and massively parallel sequencing. Nat. Methods. 2007;4:651–657. - PubMed
-
- Stormo GD, Zhao Y. Determining the specificity of protein-DNA interactions. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010;11:751–760. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

