Adenoid ameloblastoma with dentinoid
- PMID: 22923903
- PMCID: PMC3424947
- DOI: 10.4103/0973-029X.99088
Adenoid ameloblastoma with dentinoid
Abstract
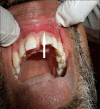
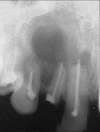
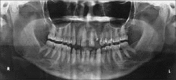
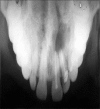
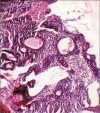
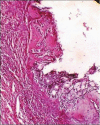
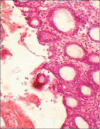
Ameloblastomas seldom cause diagnostic difficulties due to classic histopathological presentations. Adenoid ameloblastoma is a rare variant in this category which can cause problem in diagnosis due to the presence of areas resembling adenomatoid odontogenic tumor (AOT) and occurrence of varying degrees of dentinoid formation. In this article, we report a case of adenoid ameloblastoma with dentinoid, which was diagnosed accurately after the third recurrence. To the best of our knowledge, so far, only 13 cases have been reported of tumors that histologically show features of amelobalstoma and AOT with hard tissue formation. The recurrences were due to under diagnosis of the lesion followed by a conservative treatment.
Keywords: Adenoid ameloblastoma; adenomatoid odontogenic tumor; ameloblastoma; dentinoid.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Adenoid ameloblastoma with dentinoid is molecularly different from ameloblastomas and adenomatoid odontogenic tumors.J Oral Pathol Med. 2021 Nov;50(10):1067-1071. doi: 10.1111/jop.13243. Epub 2021 Sep 29. J Oral Pathol Med. 2021. PMID: 34549835
-
Atypical plexiform ameloblastoma with dentinoid: adenoid ameloblastoma with dentinoid.J Oral Pathol Med. 2001 Apr;30(4):251-4. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0714.2001.300410.x. J Oral Pathol Med. 2001. PMID: 11302246 Review.
-
Diagnostic Enigma of Adenoid Ameloblastoma: Literature Review Based Evidence to Consider It as a New Sub Type of Ameloblastoma.Head Neck Pathol. 2022 Jun;16(2):344-352. doi: 10.1007/s12105-021-01358-w. Epub 2021 Jul 19. Head Neck Pathol. 2022. PMID: 34282559 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A rare case of peripheral adenoid ameloblastoma with dentinoid.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2023 Jan;135(1):e10-e13. doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2022.08.015. Epub 2022 Sep 7. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2023. PMID: 36396590
-
Adenoid ameloblastoma with dentinoid: A rare hybrid odontogenic tumor.Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2024 Apr 1;67(2):441-444. doi: 10.4103/ijpm.ijpm_186_22. Epub 2023 Jul 6. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38391318
Cited by
-
Histopathological Insight of a Case of Adenoid Ameloblastoma: A Rare Odontogenic Tumor.Case Rep Dent. 2024 Apr 29;2024:8366045. doi: 10.1155/2024/8366045. eCollection 2024. Case Rep Dent. 2024. PMID: 38716224 Free PMC article.
-
Adenoid ameloblastoma with dentinoid: A rare hybrid variant.J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2017 May-Aug;21(2):319. doi: 10.4103/jomfp.JOMFP_53_15. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28932051 Free PMC article.
-
Update on Odontogenic Tumors: Proceedings of the North American Head and Neck Pathology Society.Head Neck Pathol. 2019 Sep;13(3):457-465. doi: 10.1007/s12105-019-01013-5. Epub 2019 Mar 18. Head Neck Pathol. 2019. PMID: 30887391 Free PMC article.
-
Odontogenic carcinosarcoma with dentinoid: a rare case report.J Int Med Res. 2021 Sep;49(9):3000605211045555. doi: 10.1177/03000605211045555. J Int Med Res. 2021. PMID: 34586932 Free PMC article.
-
Odontogenic carcinoma with dentinoid: a new odontogenic carcinoma.Head Neck Pathol. 2014 Dec;8(4):421-31. doi: 10.1007/s12105-014-0586-9. Epub 2014 Nov 20. Head Neck Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25409850 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Slabbert H, Altini M, Crooks J, Uys P. Ameloblastoma with dentinoid induction: dentinoameloblastoma. J Oral Pathol Med. 1992;21:46–8. - PubMed
-
- Ghasemi-Moridani S, Yazdi I. Adenoid ameloblastoma with dentinoid: A case report. Arch Iran Med. 2008;11:110–2. - PubMed
-
- Fukaya M, Sato H, Umakoshi H, Kurauti T, Hanzi J. A case report of adenoameloblastoma on the maxilla. Japanese Journal of Oral Surgery. 1971;17:155–8. - PubMed
-
- Chuan-Xiang Z, Yan G. Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor: A report of a rare case with recurrence. J Oral Pathol Med. 2007;36:440–3. - PubMed
-
- Takigami M, Uede T, Imaizumi T, Ohtaki M, Tanabe S, Hashi K. A case of adenomatoid odontogenic tumor with intracranial extension. Neurological Surgery. 1988;16:775–9. - PubMed

