Sub-acute effect of N(G)-nitro-l-arginine methyl-ester (L-NAME) on biochemical indices in rats: Protective effects of Kolaviron and extract of Curcuma longa L
- PMID: 22923949
- PMCID: PMC3424838
- DOI: 10.4103/0974-8490.99071
Sub-acute effect of N(G)-nitro-l-arginine methyl-ester (L-NAME) on biochemical indices in rats: Protective effects of Kolaviron and extract of Curcuma longa L
Abstract
Background: Kolaviron (KV) (biflavonoid from Garcinia kola) and extract of Curcuma longa (CL) are frequently used in folk medicine for treatment of hypertension. One of their mechanisms of action is to enhance antioxidant properties in animals. N(G)- nitro- l- arginine methyl- ester (L- NAME) is L- arginine analogue, which by binding to Nitric Oxide Synthase (NOS) may induce hypertension partly due to increase in tissues oxidative stress.
Objectives: To investigate the effect of L- NAME on some biochemical indices and the possible protective effect of KV or CL.
Materials and methods: Four groups consisting of 6 rats each were used. One group served as control, second group received L- NAME (40 mg/kg/day). Third and fourth groups were treated with KV and CL, respectively and also received L- NAME. KV and CL were given at a dose of 200 mg/kg/day.
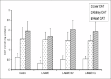
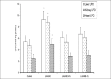
Results: L- NAME caused a significant (P <0.05) increase in the levels of serum urea, creatine kinase and alanine aminotransferase relative to controls. L- NAME treated rats had markedly decreased hepatic catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione- S- transferase (GST) and reduced glutathione (GSH) levels. Precisely, L- NAME decreased CAT, SOD, GST and GSH by 48, 52, 76 and 40%, respectively. L- NAME intoxication significantly decreased (P <0.05) renal GSH and SOD levels. Also, L- NAME caused a significant (P <0.05) induction of lipid peroxidation (LPO) in the animals. Administration of KV or CL with L- NAME caused significant (P <0.05) inhibition of LPO and augments tissue antioxidant indices.
Conclusion: These results confirm the adverse effect of L- NAME on biochemical indices and, the ability of kolaviron or Curcuma longa to ameliorate the alterations.
Keywords: Antioxidant; Curcuma longa; NG - nitro- l- arginine methyl ester; biochemical indices; kolaviron.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Kelm M, Schrader J. Control of coronary vascular tone by nitric oxide. Circ Res. 1990;66:1561–75. - PubMed
-
- Roczniak A, Burns KD. Nitric oxide stimulates guanylate cyclase and regulates sodium transport in rabbit proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1996;270:F106–15. - PubMed
-
- Kone BC, Higham S. Nitric oxide inhibits transcription of the Na+-K+ ATPase α1-subunit gene in an MTAL cell line. Am J Physiol. 1999;276:F614–21. - PubMed
-
- Takemoto M, Egashira K, Usui M, Numaguchi K, Tomita H, Tsutsui H, et al. Important role of tissue angiotensin-converting enzyme activity in the pathogenesis of coronary vascular and myocardial structural changes induced by long-term blockade of nitric oxide synthesis in rats. J Clin Invest. 1997;99:278–87. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Koyanagi M, Egashira K, Kitamoto S, Ni W, Shimokawa H, Takeya M, et al. Role of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in cardiovascular remodeling induced by chronic blockade of nitric oxide synthesis. Circulation. 2000;102:2243–48. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
