Novel approach for the management of sub-massive pulmonary embolism
- PMID: 22924075
- PMCID: PMC3425049
- DOI: 10.4103/1817-1737.98850
Novel approach for the management of sub-massive pulmonary embolism
Abstract
Background: Right ventricular (RV) dysfunction has been identified as a poor prognostic indicator in sub-massive pulmonary embolism (SPE). We hypothesized that using selective vasodilator agent is beneficial in improving RV function in patients with this condition.
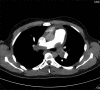
Methods: We used inhaled prostacyclin analogue (Iloprost, Ventavis(®)) in five patients with SPE. Helical computerized tomography angiogram was confirmatory for pulmonary embolism and echocardiography was used to evaluate the RV status. All patients received inhaled Iloprost, 2.5 to 5 μg every 4 hours for 3 weeks.
Results: Patients were prospectively followed for 3 months. They were assessed at baseline before starting Iloprost treatment and at 3 days, 3 weeks, and 3 months after treatment. All patients showed significant improvement in their functional class, Borg dyspnea score, NT pro-BNP level, and echocardiographic parameters.
Conclusion: In SPE, directing therapy toward decreasing pulmonary vascular resistance improves the associated pulmonary hemodynamic compromise and improves RV function.
Keywords: Iloprost; pulmonary hypertension; pulmonary vascular resistance; right ventricular function; sub-massive pulmonary embolism.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Konstantinides S, Geibel A, Olschewski M, Heinrich F, Grosser K, Rauber K, et al. Association between thrombolytic treatment and the prognosis of hemodynamically stable patients with major pulmonary embolism: results of a multicenter registry. Circulation. 1997;96:882–8. - PubMed
-
- Dalen JE. The uncertain role of thrombolytic therapy in the treatment of pulmonary embolism. Arch Intern Med. 2002;162:2521–3. - PubMed
-
- Kasper W, Konstantinides S, Geibel A, Olschewski M, Heinrich F, Grosser KD, et al. Management strategies and determinants of outcome in acute major pulmonary embolism: Results of a multicenter registry. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1997;30:1165–71. - PubMed
-
- Hamel E, Pacouret G, Vincentelli D, Forissier JF, Peycher P, Pottier JM, et al. Thrombolysis or heparin therapy in massive pulmonary embolism with right ventricular dilation: Results from a 128-patient monocenter registry. Chest. 2001;120:120–5. - PubMed
-
- Smulders YM. Pathophysiologu and treatment of hemodynamic instability in acute pulmonary embolism: The pivotal role of pulmonary vasoconstriction. Cardiovasc Res. 2000;48:23–33. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials