Patent foramen ovale in severe obstructive sleep apnea: clinical features and effects of closure
- PMID: 22924163
- PMCID: PMC5991552
- DOI: 10.1378/chest.12-0334
Patent foramen ovale in severe obstructive sleep apnea: clinical features and effects of closure
Abstract
Background: Patent foramen ovale (PFO) may contribute to nocturnal desaturation in patients with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), and the effect of PFO closure in OSA is unknown. Our study tested the hypotheses that: (1) patients with severe OSA have a higher prevalence of PFO compared with healthy control subjects, (2) patients with severe OSA with clinically significant PFO experience more nocturnal desaturation than those without, and (3) PFO closure reduces nocturnal desaturation.
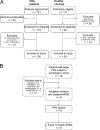
Methods: Patients with severe OSA and healthy control subjects underwent contrast transthoracic echocardiography and transcranial Doppler to detect PFO and determine shunt size. A subgroup of patients with OSA with large shunts underwent percutaneous PFO closure. Polysomnography was performed at baseline and 1, 6, and 12 months postclosure.
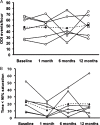
Results: One hundred patients with OSA (mean [SD] age, 52 [10] years; apnea-hypopnea index [AHI], 54 [18] events/h) and 50 control subjects (age, 52 [11] years; AHI, 2 [2] events/h) were studied. PFO prevalence was 43% in patients with OSA and 30% in control subjects ( P = .16). Large shunts were detected in 18% of patients with OSA and 6% of control subjects ( P = .049). Patients with OSA with clinically significant shunts had higher oxygen-desaturation index (ODI)/AHI ratios than patients without (ratio, 1.05 [0.27] vs 0.86 [0.26], P = .004). Six patients with OSA underwent PFO closure, which was not associated with a reduction in ODI (baseline, 48 [18]; 12 months, 51 [19] events/h; P = .92) or percentage of the night with arterial oxygen saturation , 90% (baseline, 23% [16%]; 12 months, 20% [22%]; P = .35).
Conclusions: Patients with severe OSA have a higher prevalence of PFO with large shunts compared with control subjects. The ODI/AHI ratio is increased in patients with OSA with clinically significant shunts. PFO closure does not reduce nocturnal desaturation.
Figures
Comment in
-
No closure for patent foramen ovale in obstructive sleep apnea?Chest. 2013 Feb 1;143(2):581-582. doi: 10.1378/chest.12-2216. Chest. 2013. PMID: 23381335 No abstract available.
-
Response.Chest. 2013 Feb 1;143(2):582. doi: 10.1378/chest.12-2501. Chest. 2013. PMID: 23381337 No abstract available.
-
Pathophysiology of intrapulmonary right-to-left shunt in infants with obstructive apnea.Chest. 2013 Jul;144(1):360-361. doi: 10.1378/chest.13-0566. Chest. 2013. PMID: 23880693 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hagen PT, Scholz DG, Edwards WD. Incidence and size of patent foramen ovale during the first 10 decades of life: an autopsy study of 965 normal hearts. Mayo Clin Proc. 1984;59(1):17–20. - PubMed
-
- Young T, Palta M, Dempsey J, Skatrud J, Weber S, Badr S. The occurrence of sleep-disordered breathing among middle-aged adults. N Engl J Med. 1993;328(17):1230–1235. - PubMed
-
- Peppard PE, Young T, Palta M, Skatrud J. Prospective study of the association between sleep-disordered breathing and hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2000;342(19):1378–1384. - PubMed
-
- Marin JM, Carrizo SJ, Vicente E, Agusti AG. Long-term cardiovascular outcomes in men with obstructive sleep apnoea-hypopnoea with or without treatment with continuous positive airway pressure: an observational study. Lancet. 2005;365(9464):1046–1053. - PubMed
-
- Yaggi HK, Concato J, Kernan WN, Lichtman JH, Brass LM, Mohsenin V. Obstructive sleep apnea as a risk factor for stroke and death. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(19):2034–2041. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

