Current understanding of LRRK2 in Parkinson's disease: biochemical and structural features and inhibitor design
- PMID: 22924508
- PMCID: PMC3569718
- DOI: 10.4155/fmc.12.110
Current understanding of LRRK2 in Parkinson's disease: biochemical and structural features and inhibitor design
Abstract
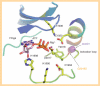
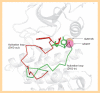
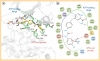
Since leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) was linked to Parkinson's disease in 2004, kinase activity of LRRK2 has been believed to play a critical role in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. As a result, identification of LRRK2 inhibitors has been a focus for drug discovery. However, most LRRK2 mutations do not simply increase kinase activity. In this review we summarize the potential mechanisms that regulate the kinase activity of LRRK2. We outline some currently available kinase inhibitors, including the identification of a DFG-out (type-II) inhibitor. Finally, we discuss the relationship of LRRK2 with tau and α-synuclein. The fact that all three proteins are autophapgy-related provides a future strategy for the identification of LRRK2 physiological substrate(s).
Figures

References
-
- Paisan-Ruiz C, Jain S, Evans EW, et al. Cloning of the gene containing mutations that cause PARK8-linked Parkinson's disease. Neuron. 2004;44:595–600. - PubMed
-
- Zimprich A, Biskup S, Leitner P, et al. Mutations in LRRK2 cause autosomal-dominant parkinsonism with pleomorphic pathology. Neuron. 2004;44:601–607. - PubMed
-
- Berg D, Schweitzer KJ, Leitner P, et al. Type and frequency of mutations in the LRRK2 gene in familial and sporadic Parkinson's disease. Brain. 2005;128:3000–3011. - PubMed
-
- Farrer M, Stone J, Mata IF, et al. LRRK2 mutations in Parkinson disease. Neurology. 2005;65:738–740. - PubMed
-
- Khan NL, Jain S, Lynch JM, et al. Mutations in the gene LRRK2 encoding dardarin (PARK8) cause familial Parkinson's disease: clinical, pathological, olfactory and functional imaging and genetic data. Brain. 2005;128:2786–2796. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
