Establishment of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor-resistant cancer cell lines and therapeutic strategies for overcoming the resistance
- PMID: 22925034
- PMCID: PMC7659208
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.12004
Establishment of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor-resistant cancer cell lines and therapeutic strategies for overcoming the resistance
Abstract
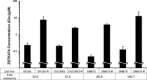
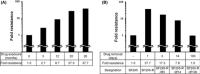
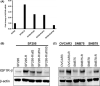
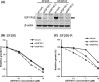
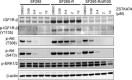
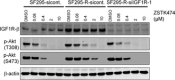
Acquired resistance is a major obstacle for conventional cancer chemotherapy, and also for some of the targeted therapies approved to date. Long-term treatment using protein tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), such as gefitinib and imatinib, gives rise to resistant cancer cells carrying a drug-resistant gatekeeper mutation in the kinase domain of the respective target genes, EGFR and BCR-ABL. As for the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitors (PI3Kis), little is known about their acquired resistance, although some are undergoing clinical trials. To address this issue, we exposed 11 human cancer cell lines to ZSTK474, a PI3Ki we developed previously, for a period of more than 1 year in vitro. Consequently, we established ZSTK474-resistant cells from four of the 11 cancer cell lines tested. The acquired resistance was not only to ZSTK474 but also to other PI3Kis. None of the PI3Ki-resistant cells, however, contained any mutation in the kinase domain of the PIK3CA gene. Instead, we found that insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R) was overexpressed in all four resistant cells. Interestingly, targeted knockdown of IGF1R expression using specific siRNAs or inhibition of IGF1R using IGF1R-TKIs reversed the acquired PI3Ki resistance. These results suggest that long-term treatment with PI3Kis may cause acquired resistance, and targeting IGF1R is a promising strategy to overcome the resistance.
© 2012 Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures

References
-
- Cantley LC. The phosphoinositide 3‐kinase pathway. Science 2002; 296: 1655–7. - PubMed
-
- Engelman JA, Luo J, Cantley LC. The evolution of phosphatidylinositol 3‐kinases as regulators of growth and metabolism. Nat Rev Genet 2006; 7: 606–19. - PubMed
-
- Samuels Y, Wang Z, Bardelli A et al High frequency of mutations of the PIK3CA gene in human cancers. Science 2004; 304: 554. - PubMed
-
- Whyte DB, Holbeck SL. Correlation of PIK3Ca mutations with gene expression and drug sensitivity in NCI‐60 cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2006; 340: 469–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

