Identification of a novel HLA-A2-restricted mutated Survivin epitope and induction of specific anti-HCC CTLs that could effectively cross-recognize wild-type Survivin antigen
- PMID: 22926105
- PMCID: PMC11028461
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-012-1323-4
Identification of a novel HLA-A2-restricted mutated Survivin epitope and induction of specific anti-HCC CTLs that could effectively cross-recognize wild-type Survivin antigen
Abstract
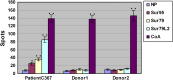
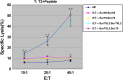
Peptide vaccine based on tumor-associated antigen (TAA), which usually belongs to self-antigen with poor immunogenicity, has been considered as an attractive option for treatment of malignant tumors. The ideal TAA epitopes should have stable affinity to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules and elicit strong anti-tumor immune response. Although point-mutation technology of TAA peptide may increase the binding capability to MHC molecules, some previous studies have revealed that part of the variant peptides results in lymphocyte not to effectively cross-recognize and kill the target tumor expressed wild-type TAA. Here, we designed a novel HLA-A2-restricted mutated TAA Survivin epitope nonapeptide Sur79L2 (KLSSGCAFL) that showed higher binding ability compared to wild-type peptide Sur79 (KHSSGCAFL) in T2-binding assays. To investigate whether Sur79L2 can induce Survivin-specific anti-hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) response, we stimulated tumor-associated lymphocytes from a HCC patient with Sur79L2 in vitro. IFN-γ release and cytotoxicity assays showed Sur79L2 could effectively cross-recognize and lysis T2 cell plus peptide Sur79 and HCC cell lines (expression of wild-type Survivin antigen) in an HLA-A2-restricted manner. In contrast, peptide Sur95 (ELTLGEFLKL) that has been reported as a very promising anti-tumor epitope in a variety of tumors except HCC were not able to generate detectable cytotoxic immune responses against HCC in this study. Our results suggest that point-mutated peptide Sur79L2 is a new HLA-A2-restricted CTL epitope and may be useful for the immunotherapy for patients with HCC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Peptide FLNPDVLDI of heparanase is a novel HLA-A2-restricted CTL epitope and elicits potent immunological antitumor effects in vitro with an 8-branched design.Oncol Rep. 2013 May;29(5):1955-61. doi: 10.3892/or.2013.2347. Epub 2013 Mar 13. Oncol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23503586
-
Efficient induction of cytotoxic T lymphocytes in hepatocellular carcinoma using the HLA-A2-restricted survivin peptide in vitro.Exp Cell Res. 2020 Jan 15;386(2):111741. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2019.111741. Epub 2019 Nov 22. Exp Cell Res. 2020. PMID: 31759968
-
Identification of a new HLA-A*0201-restricted CD8+ T cell epitope from hepatocellular carcinoma-associated antigen HCA587.Clin Exp Immunol. 2005 May;140(2):310-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2005.02786.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15807856 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of HLA-A2- or HLA-A24-restricted CTL epitopes possibly useful for glypican-3-specific immunotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2006 May 1;12(9):2689-97. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-2267. Clin Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16675560
-
Enhancing the recognition of tumour associated antigens.Folia Biol (Praha). 1994;40(1-2):74-88. Folia Biol (Praha). 1994. PMID: 7958066 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The immunogenicity of a novel cytotoxic T lymphocyte epitope from tumor antigen PL2L60 could be enhanced by 4-chlorophenylalanine substitution at position 1.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2013 Nov;62(11):1723-32. doi: 10.1007/s00262-013-1478-7. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2013. PMID: 24077852 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of an HLA-A2-restricted CD147 epitope that can induce specific CTL cytotoxicity against drug resistant MCF-7/Adr cells.Oncol Lett. 2018 Apr;15(4):6050-6056. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8085. Epub 2018 Feb 16. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29556319 Free PMC article.
-
MHC class I antigen presentation and implications for developing a new generation of therapeutic vaccines.Ther Adv Vaccines. 2014 May;2(3):77-89. doi: 10.1177/2051013614525375. Ther Adv Vaccines. 2014. PMID: 24790732 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single sample scoring of hepatocellular carcinoma: A study based on data mining.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2021 Jan-Dec;35:20587384211018389. doi: 10.1177/20587384211018389. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34053310 Free PMC article.
-
Antigen-specific T cell response from dendritic cell vaccination using side population cell-associated antigens targets hepatocellular carcinoma.Tumour Biol. 2016 Aug;37(8):11267-78. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-4935-z. Epub 2016 Mar 7. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26951511
References
-
- Zerbini A, Pilli M, Soliani P, Ziegler S, Pelosi G, Orlandini A, Cavallo C, Uggeri J, Scandroglio R, Crafa P, Spagnoli GC, Ferrari C, Missale G. Ex vivo characterization of tumor-derived melanoma antigen encoding gene-specific CD8 + cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2004;40:102–109. doi: 10.1016/S0168-8278(03)00484-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shang XY, Chen HS, Zhang HG, Pang XW, Qiao H, Peng JR, Qin LL, Fei R, Mei MH, Leng XS, Gnjatic S, Ritter G, Simpson AJ, Old LJ, Chen WF. The spontaneous CD8 + T-cell response to HLA-A2-restricted NY-ESO-1b peptide in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:6946–6955. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-0502. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

