Identification and determination of Aconitum alkaloids in Aconitum herbs and Xiaohuoluo pill using UPLC-ESI-MS
- PMID: 22926305
- PMCID: PMC6268077
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules170910242
Identification and determination of Aconitum alkaloids in Aconitum herbs and Xiaohuoluo pill using UPLC-ESI-MS
Abstract
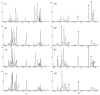
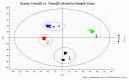
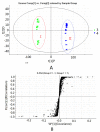
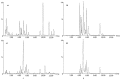
A rapid, specific, and sensitive ultra-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry (UPLC-ESI-MS) method to examine the chemical differences between Aconitum herbs and processed products has been developed and validated. Combined with chemometrics analysis of principal component analysis (PCA) and orthogonal projection to latent structural discriminate analysis, diester-diterpenoid and monoester-type alkaloids, especially the five alkaloids which contributed to the chemical distinction between Aconitum herbs and processed products, namely mesaconitine (MA), aconitine (AC), hypaconitine (HA), benzoylmesaconitine (BMA), and benzoylhypaconitine (BHA), were picked out. Further, the five alkaloids and benzoylaconitine (BAC) have been simultaneously determined in the Xiaohuoluo pill. Chromatographic separations were achieved on a C₁₈ column and peaks were detected by mass spectrometry in positive ion mode and selected ion recording (SIR) mode. In quantitative analysis, the six alkaloids showed good regression, (r) > 0.9984, within the test ranges. The lower limit quantifications (LLOQs) for MA, AC, HA, BMA, BAC, and BHA were 1.41, 1.20, 1.92, 4.28, 1.99 and 2.02 ng·mL⁻¹, respectively. Recoveries ranged from 99.7% to 101.7%. The validated method was applied successfully in the analysis of the six alkaloids from different samples, in which significant variations were revealed. Results indicated that the developed assay can be used as an appropriate quality control assay for Xiaohuoluo pill and other herbal preparations containing Aconitum roots.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Quantitative determination of diterpenoid alkaloids in four species of Aconitum by HPLC.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2006 Mar 3;40(4):1031-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2005.08.012. Epub 2005 Sep 21. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2006. PMID: 16181762
-
Quantification of Aconitum alkaloids in aconite roots by a modified RP-HPLC method.Phytochem Anal. 2005 Nov-Dec;16(6):415-21. doi: 10.1002/pca.861. Phytochem Anal. 2005. PMID: 16315485
-
Neutral fragment filtering for rapid identification of new diester-diterpenoid alkaloids in roots of Aconitum carmichaeli by ultra-high-pressure liquid chromatography coupled with linear ion trap-orbitrap mass spectrometry.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e52352. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052352. Epub 2012 Dec 21. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23285005 Free PMC article.
-
[Simultaneous determination of four trace aconitum alkaloids in urine using ultra performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry].Se Pu. 2013 Mar;31(3):211-7. doi: 10.3724/sp.j.1123.2012.10018. Se Pu. 2013. PMID: 23785992 Chinese.
-
[Chemical constituents and analytic methods of Aconitum herbal drugs].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2001 Oct;26(10):659-62. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2001. PMID: 12830825 Review. Chinese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Exploring potential chemical markers by metabolomics method for studying the processing mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine using RPLC-Q-TOF/MS: a case study of Radix Aconiti.Chem Cent J. 2013 Feb 22;7(1):36. doi: 10.1186/1752-153X-7-36. Chem Cent J. 2013. PMID: 23432780 Free PMC article.
-
Use, history, and liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry chemical analysis of Aconitum.J Food Drug Anal. 2016 Jan;24(1):29-45. doi: 10.1016/j.jfda.2015.09.001. Epub 2015 Oct 16. J Food Drug Anal. 2016. PMID: 28911407 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Study on the potential active components and molecular mechanism of Xiao Huoluo Pills in the treatment of cartilage degeneration of knee osteoarthritis based on bioinformatics analysis and molecular docking technology.J Orthop Surg Res. 2021 Jul 17;16(1):460. doi: 10.1186/s13018-021-02552-w. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021. PMID: 34273999 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the Alkaloids in Tibetan Medicine Aconitum pendulum Busch by HPLC-MSn Combined with Column Chromatography.J Chromatogr Sci. 2016 May-Jun;54(5):752-8. doi: 10.1093/chromsci/bmw002. Epub 2016 Feb 18. J Chromatogr Sci. 2016. PMID: 26896350 Free PMC article.
-
RECENT ADVANCES IN ULTRA-HIGH PERFORMANCE LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY FOR THE ANALYSIS OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE.Anal Lett. 2014;47(11):1835-1851. doi: 10.1080/00032719.2014.888727. Anal Lett. 2014. PMID: 25045170 Free PMC article.
References
-
- The State Pharmacopoeia Committee of People’s Republic of China. Pharmacopoeia of People’s Republic of China. Vol. 1. Chemical Industry Press; Beijing, China: 2010. pp. 36–38, 220–221, 509.
-
- Kita Y., Tto M. Nuclear ribosomal ITS sequences and phylogeny in East Asian Aconitum subgenus Aconitum (Ranunculaceae), with special reference to extensive polymorphism in individual plants. Plant. Syst. Evol. 2000;225:1–13. doi: 10.1007/BF00985455. - DOI
-
- Wang F.P. Chemical of Alkaloids. Chemical Industry Publishing; Beijing, China: 2008.
-
- Chen Y., Chu Y.L., Chu J.H. Alkaloids of the Chinese drugs, Aconitum Spp-IX. Alkaloids from Chuan-wu and Fu-zi, Aconitum Carmichaelidebx. Acta Phram. Sin. 1956;12:435–439. - PubMed
-
- Li Z.B., Lu G.H., Chen D.L., Wang F.P. Chemical study on the alkaloids of “Cao Wu”. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 1997;1:9–14.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

