Tissue microarray construction for salivary gland tumors study
- PMID: 22926480
- PMCID: PMC3548626
- DOI: 10.4317/medoral.18204
Tissue microarray construction for salivary gland tumors study
Abstract
Objective: To describe and discuss the design, building and usefulness of tissue microarray (TMA) blocks for the study of salivary gland tumors (SGTs).
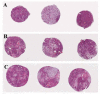
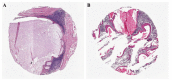
Study design: Two hundred thirty-eight formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded SGTs were arranged in blocks of TMA using a manual tissue arrayer. Three representative cores of 1.0, 2.0 or 3.0mm were taken from each original block and their characteristics were analyzed and described.
Results: It was created 12 TMA blocks that presented highly representative neoplastic cylinders. However, those neoplasias rich in cystic spaces such as mucoepidermoid carcinoma and Warthin tumor presented more difficulties to be sampled, as the neoplastic tissue available was scarce. Tissue damage and loss during TMA construction was estimated as 3.7%.
Conclusion: Representative areas of SGTs, with relatively small loss of tissue, can be obtained with the construction of TMA blocks for molecular studies. However, tumors rich in cystic spaces present more difficulties to be adequately sampled.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor immunoexpression is increased in malignant salivary gland tumors.Ann Diagn Pathol. 2015 Jun;19(3):169-74. doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2015.03.010. Epub 2015 Apr 6. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25900273
-
Immunohistochemical expression of oestrogen receptor-α and progesterone receptor in salivary gland tumours.J Oral Pathol Med. 2013 Oct;42(9):716-9. doi: 10.1111/jop.12071. Epub 2013 Apr 19. J Oral Pathol Med. 2013. PMID: 23601083
-
Tissue microarray use for immunohistochemical study of ameloblastoma.J Oral Pathol Med. 2016 Oct;45(9):704-711. doi: 10.1111/jop.12428. Epub 2016 Feb 3. J Oral Pathol Med. 2016. PMID: 26841348
-
Making a Tissue Microarray.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1897:313-323. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-8935-5_27. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30539455 Review.
-
Tissue microarrays: construction and use.Methods Mol Biol. 2013;980:13-28. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-287-2_2. Methods Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23359147 Review.
Cited by
-
Recommendations for Tissue Microarray Construction and Quality Assurance.Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2020 Apr;28(4):325-330. doi: 10.1097/PAI.0000000000000739. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2020. PMID: 31033496 Free PMC article.
-
SOX10 and GATA3 in Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma and Polymorphous Adenocarcinoma.Head Neck Pathol. 2020 Jun;14(2):406-411. doi: 10.1007/s12105-019-01046-w. Epub 2019 Jun 20. Head Neck Pathol. 2020. PMID: 31222589 Free PMC article.
-
MutSα expression predicts a lower disease-free survival in malignant salivary gland tumors: an immunohistochemical study.Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2022 Mar 1;27(2):e164-e173. doi: 10.4317/medoral.25138. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2022. PMID: 35218645 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yamazaki M, Fujii S, Murata Y, Hayashi R, Ochiai A. High expression level of geminin predicts a poor clinical outcome in salivary gland carcinomas. Histopathology. 2010;56:883–92. - PubMed
-
- Vargas PA, Gerhard R, Araújo-Filho VJ, de Castro IV. Salivary gland tumors in a Brazilian Population: A retrospective study of 124 cases. Rev Hosp Clin Fac Med Sao Paulo. 2002;57:271–6. - PubMed
-
- Simon R, Sauter G. Tissue microarrays for miniaturized high-throughput molecular profiling of tumors. Exp Hematol. 2002;30:1365–72. - PubMed
-
- Kononen J, Bubendorf L, Kallioniemi A, Bärlund M, Schraml P, Leighton S. Tissue microarrays for high-throughput molecular profiling of tumor specimens. Nat Med. 1998;4:844–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

