Activity of gallidermin on Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms
- PMID: 22926575
- PMCID: PMC3486563
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01296-12
Activity of gallidermin on Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms
Abstract
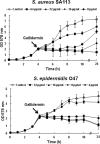
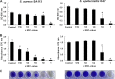
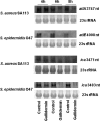
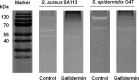
Due to their abilities to form strong biofilms, Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis are the most frequently isolated pathogens in persistent and chronic implant-associated infections. As biofilm-embedded bacteria are more resistant to antibiotics and the immune system, they are extremely difficult to treat. Therefore, biofilm-active antibiotics are a major challenge. Here we investigated the effect of the lantibiotic gallidermin on two representative biofilm-forming staphylococcal species. Gallidermin inhibits not only the growth of staphylococci in a dose-dependent manner but also efficiently prevents biofilm formation by both species. The effect on biofilm might be due to repression of biofilm-related targets, such as ica (intercellular adhesin) and atl (major autolysin). However, gallidermin's killing activity on 24-h and 5-day-old biofilms was significantly decreased. A subpopulation of 0.1 to 1.0% of cells survived, comprising "persister" cells of an unknown genetic and physiological state. Like many other antibiotics, gallidermin showed only limited activity on cells within mature biofilms.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The lantibiotic gallidermin acts bactericidal against Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus aureus and antagonizes the bacteria-induced proinflammatory responses in dermal fibroblasts.Microbiologyopen. 2018 Dec;7(6):e00606. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.606. Epub 2018 Mar 13. Microbiologyopen. 2018. PMID: 29536668 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-biofilm activity of sub-inhibitory povidone-iodine concentrations against Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus aureus.J Orthop Res. 2010 Sep;28(9):1252-6. doi: 10.1002/jor.21110. J Orthop Res. 2010. PMID: 20187117
-
Effect of Antimicrobial and Physical Treatments on Growth of Multispecies Staphylococcal Biofilms.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017 May 31;83(12):e03483-16. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03483-16. Print 2017 Jun 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28411222 Free PMC article.
-
ica and beyond: biofilm mechanisms and regulation in Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus aureus.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2007 May;270(2):179-88. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2007.00688.x. Epub 2007 Apr 10. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2007. PMID: 17419768 Review.
-
The Staphylococcal Biofilm: Adhesins, Regulation, and Host Response.Microbiol Spectr. 2016 Apr;4(2):10.1128/microbiolspec.VMBF-0022-2015. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.VMBF-0022-2015. Microbiol Spectr. 2016. PMID: 27227309 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The "Cins" of Our Fathers: Rejuvenated Interest in Colicins to Combat Drug Resistance.J Microbiol. 2023 Feb;61(2):145-158. doi: 10.1007/s12275-023-00023-x. Epub 2023 Feb 8. J Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36753040 Review.
-
Antibacterial and Biofilm Modulating Potential of Ferulic Acid-Grafted Chitosan against Human Pathogenic Bacteria.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jul 24;19(8):2157. doi: 10.3390/ijms19082157. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30042337 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Application of Lantibiotics and Other Lanthipeptides: Old and New Findings.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2021 Jun 25;87(14):e0018621. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00186-21. Epub 2021 Jun 25. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33962984 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Staphylococcal Biofilm Development: Structure, Regulation, and Treatment Strategies.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2020 Aug 12;84(3):e00026-19. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00026-19. Print 2020 Aug 19. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2020. PMID: 32792334 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GC/MS Profiling, Antibacterial, Anti-Quorum Sensing, and Antibiofilm Properties of Anethum graveolens L. Essential Oil: Molecular Docking Study and In-Silico ADME Profiling.Plants (Basel). 2023 May 16;12(10):1997. doi: 10.3390/plants12101997. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37653914 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Augustin J, et al. 1992. Genetic analysis of epidermin biosynthetic genes and epidermin-negative mutants of Staphylococcus epidermidis. Eur. J. Biochem. 204:1149–1154 - PubMed
-
- Bierbaum G, Brötz H, Koller KP, Sahl HG. 1995. Cloning, sequencing and production of the lantibiotic mersacidin. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 127:121–126 - PubMed
-
- Brötz H, et al. 1998. Role of lipid-bound peptidoglycan precursors in the formation of pores by nisin, epidermin and other lantibiotics. Mol. Microbiol. 30:317–327 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

