Mechanism of platelet dense granule biogenesis: study of cargo transport and function of Rab32 and Rab38 in a model system
- PMID: 22927249
- PMCID: PMC3496959
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2012-04-420745
Mechanism of platelet dense granule biogenesis: study of cargo transport and function of Rab32 and Rab38 in a model system
Abstract
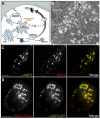
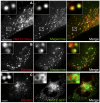
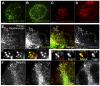
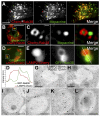
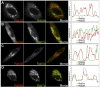
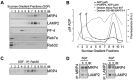
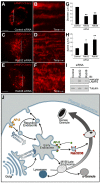
Dense granules are important in platelet aggregation to form a hemostatic plug as evidenced by the increased bleeding time in mice and humans with dense granule deficiency. Dense granules also are targeted by antiplatelet agents because of their role in thrombus formation. Therefore, the molecular understanding of the dense granule and its biogenesis is of vital importance. In this work, we establish a human megakaryocytic cell line (MEG-01) as a model system for the study of dense granule biogenesis using a variety of cell biology and biochemical approaches. Using this model system, we determine the late endocytic origin of these organelles by colocalization of the internalized fluid phase marker dextran with both mepacrine and transmembrane dense granule proteins. By mistargeting of mutant dense granule proteins, we demonstrate that sorting signals recognized by adaptor protein-3 are necessary for normal transport to dense granules. Furthermore, we show that tissue-specific Rab32 and Rab38 are crucial for the fusion of vesicles containing dense granule cargo with the maturing organelle. This work sheds light on the biogenesis of dense granules at the molecular level and opens the possibility of using this powerful model system for the investigation of new components of the biogenesis machinery.
Figures
Comment in
-
Monitoring granule traffic in megakaryocytes.Blood. 2012 Nov 8;120(19):3869-70. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-09-455121. Blood. 2012. PMID: 23144159 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

