Interleukin-27 receptor limits atherosclerosis in Ldlr-/- mice
- PMID: 22927332
- PMCID: PMC3750996
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.112.277525
Interleukin-27 receptor limits atherosclerosis in Ldlr-/- mice
Abstract
Rationale: Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disease of the arterial wall. Several proinflammatory cytokines are known to promote atherosclerosis, but less is known about the physiological role of anti-inflammatory cytokines. Interleukin (IL)-27 is a recently discovered member of the IL-6/IL-12 family. The IL-27 receptor is composed of IL-27 receptor A (WSX-1) and gp130 and is required for all established IL-27 signaling pathways. The expression of the IL-27 subunit Ebi3 is elevated in human atheromas, yet its function in atherosclerosis remains unknown.
Objective: The aim of this study was to test the role of IL-27 receptor signaling in immune cells in atherosclerosis development.
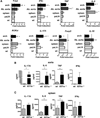
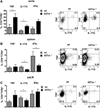
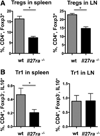
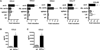
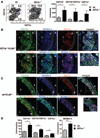
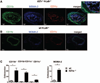
Methods and results: Atherosclerosis-prone Ldlr(-/-) mice transplanted with Il27ra(-/-) bone marrow and fed Western diet for 16 weeks developed significantly larger atherosclerotic lesions in aortic roots, aortic arches, and abdominal aortas. Augmented disease correlated with increased accumulation of CD45(+) leukocytes and CD4(+) T cells in the aorta, which produced increased amounts of IL-17A and tumor necrosis factor. Several chemokines, including CCL2, were upregulated in the aortas of Ldlr(-/-) mice receiving Il27ra(-/-) bone marrow, resulting in accumulation of CD11b(+) and CD11c(+) macrophages and dendritic cells in atherosclerotic aortas.
Conclusions: The absence of anti-inflammatory IL-27 signaling skews immune responses toward T-helper 17, resulting in increased production of IL-17A and tumor necrosis factor, which in turn enhances chemokine expression and drives the accumulation of proatherogenic myeloid cells in atherosclerotic aortas. These findings establish a novel antiatherogenic role for IL-27 receptor signaling, which acts to suppress the production of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines and to curb the recruitment of inflammatory myeloid cells into atherosclerotic aortas.
Figures


References
-
- Ait-Oufella H, Taleb S, Mallat Z, Tedgui A. Recent advances on the role of cytokines in atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011;31:969–979. - PubMed
-
- Zernecke A, Weber C. Chemokines in the vascular inflammatory response of atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc Res. 2010;86:192–201. - PubMed
-
- Buono C, Come CE, Stavrakis G, Maguire GF, Connelly PW, Lichtman AH. Influence of interferon-gamma on the extent and phenotype of diet-induced atherosclerosis in the LDLR-deficient mouse. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2003;23:454–460. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

