Insulin stimulation of SREBP-1c processing in transgenic rat hepatocytes requires p70 S6-kinase
- PMID: 22927400
- PMCID: PMC3479583
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1213343109
Insulin stimulation of SREBP-1c processing in transgenic rat hepatocytes requires p70 S6-kinase
Abstract
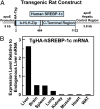
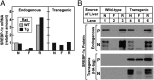
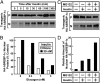
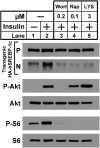
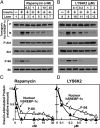
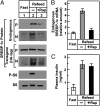
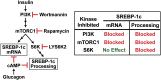
Insulin activates sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c) in liver, thereby increasing fatty acid and triglyceride synthesis. We created a line of transgenic rats that produce epitope-tagged human SREBP-1c in liver under control of the constitutive apolipoprotein E promoter/enhancer. This system allows us to dissect the pathway by which insulin stimulates SREBP-1c processing without interference by the insulin-mediated increase in SREBP-1c mRNA. Rats are used because freshly isolated rat hepatocytes respond much more robustly to insulin than do mouse hepatocytes. The data reveal that insulin-mediated stimulation of SREBP-1c processing requires the mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1), which also is required for insulin-mediated SREBP-1c mRNA induction. However, in contrast to mRNA induction, insulin stimulation of SREBP-1c processing is blocked by an inhibitor of p70 S6-kinase. The data indicate that the pathways for insulin enhancement of SREBP-1c mRNA and proteolytic processing diverge after mTORC1. Stimulation of processing requires the mTORC1 target p70 S6-kinase, whereas induction of mRNA bypasses this enzyme. Insulin stimulation of both processes is blocked by glucagon. The transgenic rat system will be useful in further defining the molecular mechanism for insulin stimulation of lipid synthesis in liver in normal and diabetic states.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Distinct mTORC1 pathways for transcription and cleavage of SREBP-1c.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Oct 2;109(40):15974-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1214113109. Epub 2012 Sep 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23012450 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Docosahexaenoic acid inhibits proteolytic processing of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c) via activation of AMP-activated kinase.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Dec;1851(12):1521-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2015.08.007. Epub 2015 Aug 29. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 26327595
-
Insulin-induced de novo lipid synthesis occurs mainly via mTOR-dependent regulation of proteostasis of SREBP-1c.Mol Cell Biochem. 2020 Jan;463(1-2):13-31. doi: 10.1007/s11010-019-03625-5. Epub 2019 Sep 20. Mol Cell Biochem. 2020. PMID: 31541353
-
Bifurcation of insulin signaling pathway in rat liver: mTORC1 required for stimulation of lipogenesis, but not inhibition of gluconeogenesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Feb 23;107(8):3441-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0914798107. Epub 2010 Feb 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20133650 Free PMC article.
-
Connecting mTORC1 signaling to SREBP-1 activation.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2012 Jun;23(3):226-234. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0b013e328352dd03. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2012. PMID: 22449814 Review.
-
Hepatic steatosis: a role for de novo lipogenesis and the transcription factor SREBP-1c.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2010 Oct;12 Suppl 2:83-92. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2010.01275.x. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2010. PMID: 21029304 Review.
Cited by
-
A pathway approach to investigate the function and regulation of SREBPs.Genes Nutr. 2013 May;8(3):289-300. doi: 10.1007/s12263-013-0342-x. Epub 2013 Mar 21. Genes Nutr. 2013. PMID: 23516131 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular logic of mTORC1 signalling as a metabolic rheostat.Nat Metab. 2019 Mar;1(3):321-333. doi: 10.1038/s42255-019-0038-7. Epub 2019 Mar 4. Nat Metab. 2019. PMID: 32694720 Review.
-
Roles of Vitamin A Metabolism in the Development of Hepatic Insulin Resistance.ISRN Hepatol. 2013 Sep 30;2013:534972. doi: 10.1155/2013/534972. eCollection 2013. ISRN Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 27335827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unraveling the intricate relationship between lipid metabolism and oncogenic signaling pathways.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Jun 12;12:1399065. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1399065. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38933330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphorylation of Insig-2 mediates inhibition of fatty acid synthesis by polyunsaturated fatty acids.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Aug 20;121(34):e2409262121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2409262121. Epub 2024 Aug 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39145929 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

