Low-density lipoprotein receptor overexpression enhances the rate of brain-to-blood Aβ clearance in a mouse model of β-amyloidosis
- PMID: 22927427
- PMCID: PMC3458349
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1206446109
Low-density lipoprotein receptor overexpression enhances the rate of brain-to-blood Aβ clearance in a mouse model of β-amyloidosis
Abstract
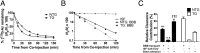
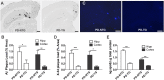
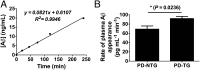
The apolipoprotein E (APOE)-ε4 allele is the strongest genetic risk factor for late-onset, sporadic Alzheimer's disease, likely increasing risk by altering amyloid-β (Aβ) accumulation. We recently demonstrated that the low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) is a major apoE receptor in the brain that strongly regulates amyloid plaque deposition. In the current study, we sought to understand the mechanism by which LDLR regulates Aβ accumulation by altering Aβ clearance from brain interstitial fluid. We hypothesized that increasing LDLR levels enhances blood-brain barrier-mediated Aβ clearance, thus leading to reduced Aβ accumulation. Using the brain Aβ efflux index method, we found that blood-brain barrier-mediated clearance of exogenously administered Aβ is enhanced with LDLR overexpression. We next developed a method to directly assess the elimination of centrally derived, endogenous Aβ into the plasma of mice using an anti-Aβ antibody that prevents degradation of plasma Aβ, allowing its rate of appearance from the brain to be measured. Using this plasma Aβ accumulation technique, we found that LDLR overexpression enhances brain-to-blood Aβ transport. Together, our results suggest a unique mechanism by which LDLR regulates brain-to-blood Aβ clearance, which may serve as a useful therapeutic avenue in targeting Aβ clearance from the brain.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: D.M.H. cofounded C2N Diagnostics. Some measurements of samples were assessed by employees of C2N Diagnostics. D.M.H. is on the scientific advisory boards of Satori and En Vivo, and consults for Pfizer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Innogenetics.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AG023084/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG023084/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AG023084/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NS34467/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- AG13956/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AG013956/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG034004/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30-NS057105/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F31 AG034004/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG029481/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS057105/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 NS034467/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG013956/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG029481/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NS034467/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS034467/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

