Polyunsaturated fatty acid concentration predicts myelin integrity in early-phase psychosis
- PMID: 22927668
- PMCID: PMC3686450
- DOI: 10.1093/schbul/sbs089
Polyunsaturated fatty acid concentration predicts myelin integrity in early-phase psychosis
Abstract
Background: White matter (WM) abnormalities have been implicated in schizophrenia, yet the mechanisms underlying these abnormalities are not fully understood. Several lines of evidence suggest that polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) play a role in myelination, and there is substantial evidence documenting decreased PUFA concentrations in schizophrenia. We therefore hypothesized that lower membrane PUFA concentrations may be related to reduced WM integrity in schizophrenia and related disorders.
Methods: In 30 male patients with a recent-onset psychotic disorder, erythrocyte membrane PUFA concentrations were assessed and diffusion tensor imaging was performed with voxelwise analysis.
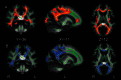
Results: Lower total PUFA concentration was associated with lower fractional anisotropy (FA) throughout the corpus callosum and bilateral parietal, occipital, temporal and frontal WM (P < .05, corrected). Of the individual PUFAs, lower arachidonic acid concentration, and to a lesser extent, lower nervonic acid, linoleic acid, and docosapentaenoic acid concentration were significantly associated with lower FA. PUFA concentrations were inversely associated with radial diffusivity but showed little association with axial diffusivity. Greater severity of negative symptoms was associated with lower nervonic acid concentration and lower FA values.
Conclusions: Membrane PUFA concentrations appear to be robustly related to brain WM integrity in early phase psychosis. These findings may provide a basis for studies to investigate the effects of PUFA supplementation on WM integrity and associated symptomatology in early psychosis.
Keywords: diffusion tensor imaging; first-episode psychosis; myelin; polyunsaturated fatty acids; schizophrenia; white matter.
Figures

References
-
- Li D, Collier DA, He L. Meta-analysis shows strong positive association of the neuregulin 1 (NRG1) gene with schizophrenia. Hum Mol Genet. 2006;15:1995–2002 - PubMed
-
- Tkachev D, Mimmack ML, Ryan MM, et al. Oligodendrocyte dysfunction in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Lancet. 2003;362:798–805 - PubMed
-
- Hof PR, Haroutunian V, Copland C, Davis KL, Buxbaum JD. Molecular and cellular evidence for an oligodendrocyte abnormality in schizophrenia. Neurochem Res. 2002;27:1193–1200 - PubMed
-
- Peters BD, Blaas J, de Haan L. Diffusion tensor imaging in the early phase of schizophrenia: what have we learned? J Psychiatr Res. 2010;44:993–1004 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

