The Irish potato famine pathogen Phytophthora infestans translocates the CRN8 kinase into host plant cells
- PMID: 22927814
- PMCID: PMC3426532
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002875
The Irish potato famine pathogen Phytophthora infestans translocates the CRN8 kinase into host plant cells
Erratum in
-
Correction: The Irish potato famine pathogen Phytophthora infestans translocates the CRN8 kinase into host plant cells.PLoS Pathog. 2015 Mar 25;11(3):e1004753. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004753. eCollection 2015 Mar. PLoS Pathog. 2015. PMID: 25806799 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
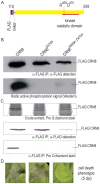
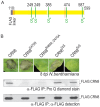
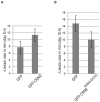
Phytopathogenic oomycetes, such as Phytophthora infestans, secrete an arsenal of effector proteins that modulate plant innate immunity to enable infection. We describe CRN8, a host-translocated effector of P. infestans that has kinase activity in planta. CRN8 is a modular protein of the CRN effector family. The C-terminus of CRN8 localizes to the host nucleus and triggers cell death when the protein is expressed in planta. Cell death induction by CRN8 is dependent on its localization to the plant nucleus, which requires a functional nuclear localization signal (NLS). The C-terminal sequence of CRN8 has similarity to a serine/threonine RD kinase domain. We demonstrated that CRN8 is a functional RD kinase and that its auto-phosphorylation is dependent on an intact catalytic site. Co-immunoprecipitation experiments revealed that CRN8 forms a dimer or multimer. Heterologous expression of CRN8 in planta resulted in enhanced virulence by P. infestans. In contrast, in planta expression of the dominant-negative CRN8(R469A;D470A) resulted in reduced P. infestans infection, further implicating CRN8 in virulence. Overall, our results indicate that similar to animal parasites, plant pathogens also translocate biochemically active kinase effectors inside host cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





Comment in
-
Plant pathogens: Oomycete kinase blights potatoes.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2012 Oct;10(10):672. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2884. Epub 2012 Sep 10. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22961339 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Potato NPH3/RPT2-Like Protein StNRL1, Targeted by a Phytophthora infestans RXLR Effector, Is a Susceptibility Factor.Plant Physiol. 2016 May;171(1):645-57. doi: 10.1104/pp.16.00178. Epub 2016 Mar 10. Plant Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26966171 Free PMC article.
-
An effector of the Irish potato famine pathogen antagonizes a host autophagy cargo receptor.Elife. 2016 Jan 14;5:e10856. doi: 10.7554/eLife.10856. Elife. 2016. PMID: 26765567 Free PMC article.
-
Divergent Evolution of PcF/SCR74 Effectors in Oomycetes Is Associated with Distinct Recognition Patterns in Solanaceous Plants.mBio. 2020 Jun 30;11(3):e00947-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00947-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32605983 Free PMC article.
-
The cell biology of late blight disease.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2016 Dec;34:127-135. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2016.09.002. Epub 2016 Oct 7. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27723513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effector-triggered immunity by the plant pathogen Phytophthora.Trends Microbiol. 2006 Nov;14(11):470-3. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2006.09.004. Epub 2006 Sep 25. Trends Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16996740 Review.
Cited by
-
Arms race: diverse effector proteins with conserved motifs.Plant Signal Behav. 2019;14(2):1557008. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2018.1557008. Epub 2019 Jan 9. Plant Signal Behav. 2019. PMID: 30621489 Free PMC article.
-
Two cytoplasmic effectors of Phytophthora sojae regulate plant cell death via interactions with plant catalases.Plant Physiol. 2015 Jan;167(1):164-75. doi: 10.1104/pp.114.252437. Epub 2014 Nov 25. Plant Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25424308 Free PMC article.
-
The effector candidate repertoire of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Rhizophagus clarus.BMC Genomics. 2016 Feb 9;17:101. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2422-y. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 26861502 Free PMC article.
-
Time-resolved dual transcriptomics reveal early induced Nicotiana benthamiana root genes and conserved infection-promoting Phytophthora palmivora effectors.BMC Biol. 2017 May 11;15(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s12915-017-0379-1. BMC Biol. 2017. PMID: 28494759 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative Proteomics of Potato Leaves Infected with Phytophthora infestans Provides Insights into Coordinated and Altered Protein Expression during Early and Late Disease Stages.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jan 1;20(1):136. doi: 10.3390/ijms20010136. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30609684 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lamour K, Kamoun S (2009) Oomycete genetics and genomics: diversity, interactions and research tools. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley-Blackwell.
-
- van Damme M, Cano LM, Oliva R, Schornack S, Segretin ME, et al... (2011) Evolutionary and Functional Dynamics of Oomycete Effector Genes. In: Effectors in Plant–Microbe Interactions. Wiley-Blackwell. pp. 101–120.
-
- Chisholm ST, Coaker G, Day B, Staskawicz BJ (2006) Host-microbe interactions: shaping the evolution of the plant immune response. Cell 124: 803–814. - PubMed
-
- Kamoun S (2007) Groovy times: filamentous pathogen effectors revealed. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10: 358–365. - PubMed
-
- Hogenhout SA, Van der Hoorn RA, Terauchi R, Kamoun S (2009) Emerging concepts in effector biology of plant-associated organisms. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 22: 115–122. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

